NoCode Template Builder
In the following documentation, we will explore the utilization of StackGuardian's NoCode Template Builder for creating and configuring templates. Additionally, we will delve into the various custom UI widgets introduced, understand the SG noCode tab, and provide examples for using these widgets in your templates.
The NoCode Template Builder allows users to build and configure templates using JSONSchema Form representation of input JSON data, providing a streamlined experience for creating Orchestrator Workflows without needing extensive coding knowledge.
The NoCode interface enables flexible UI structuring for a seamless user experience. Explore its capabilities at React JSONSchema Form.
Navigating the NoCode Template Builder
- Navigate to Orchestrator > Library > select one of the subscribed templates.
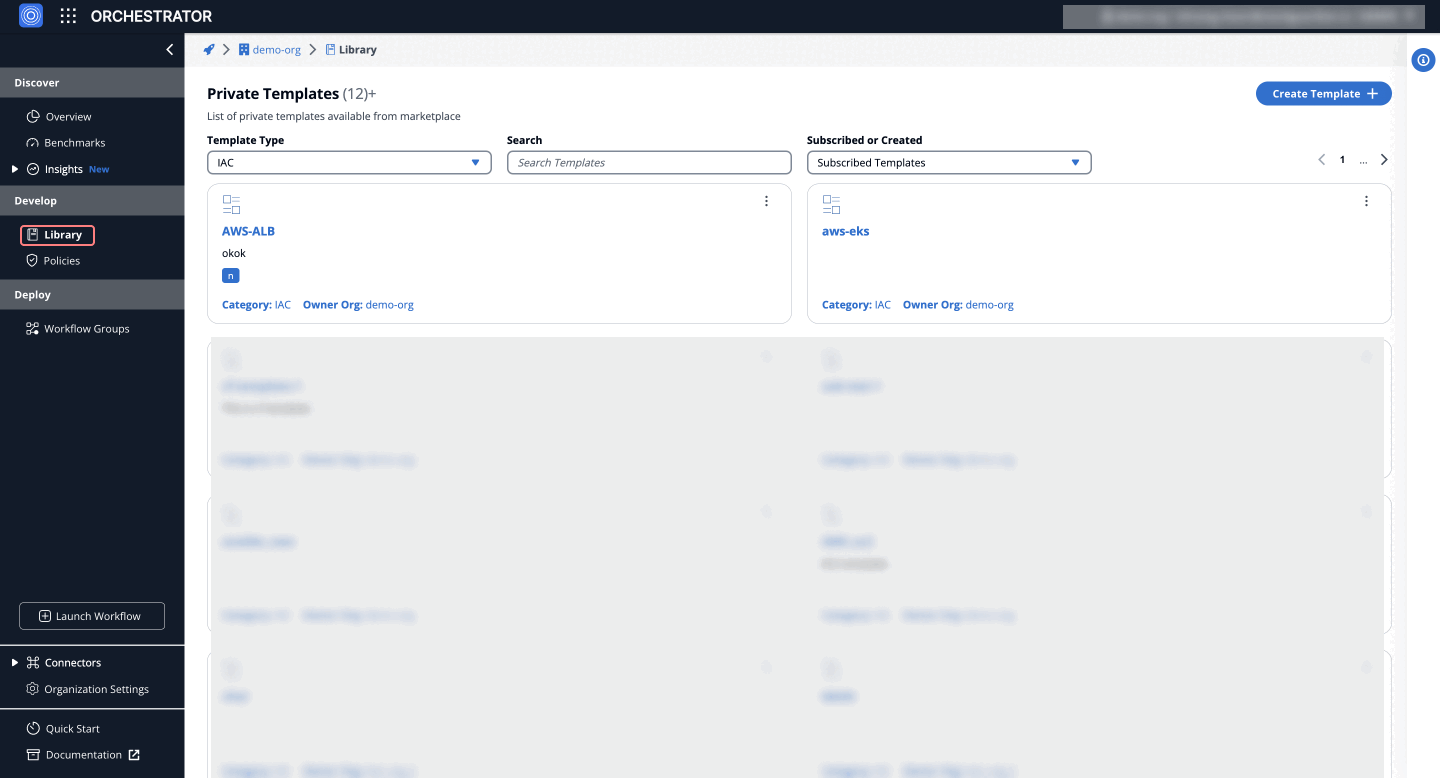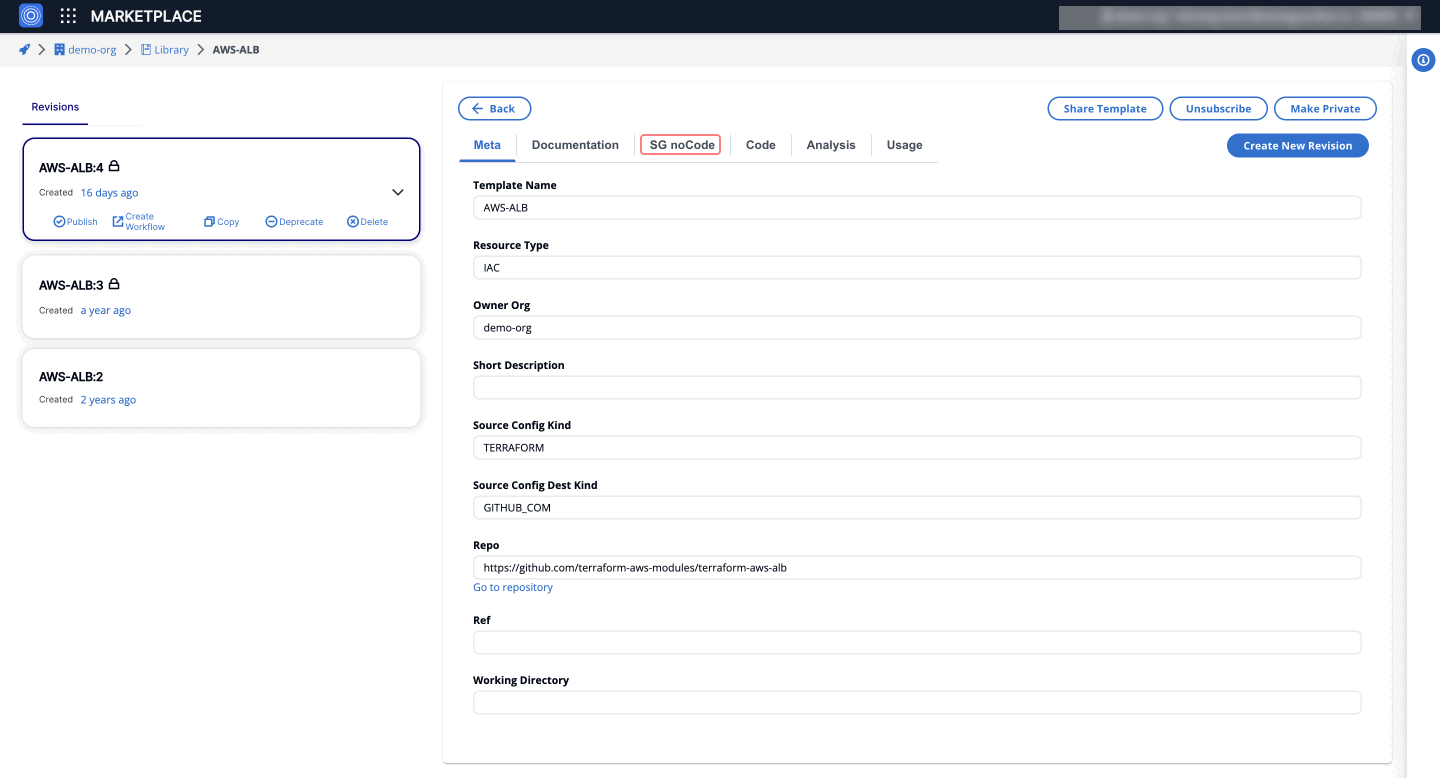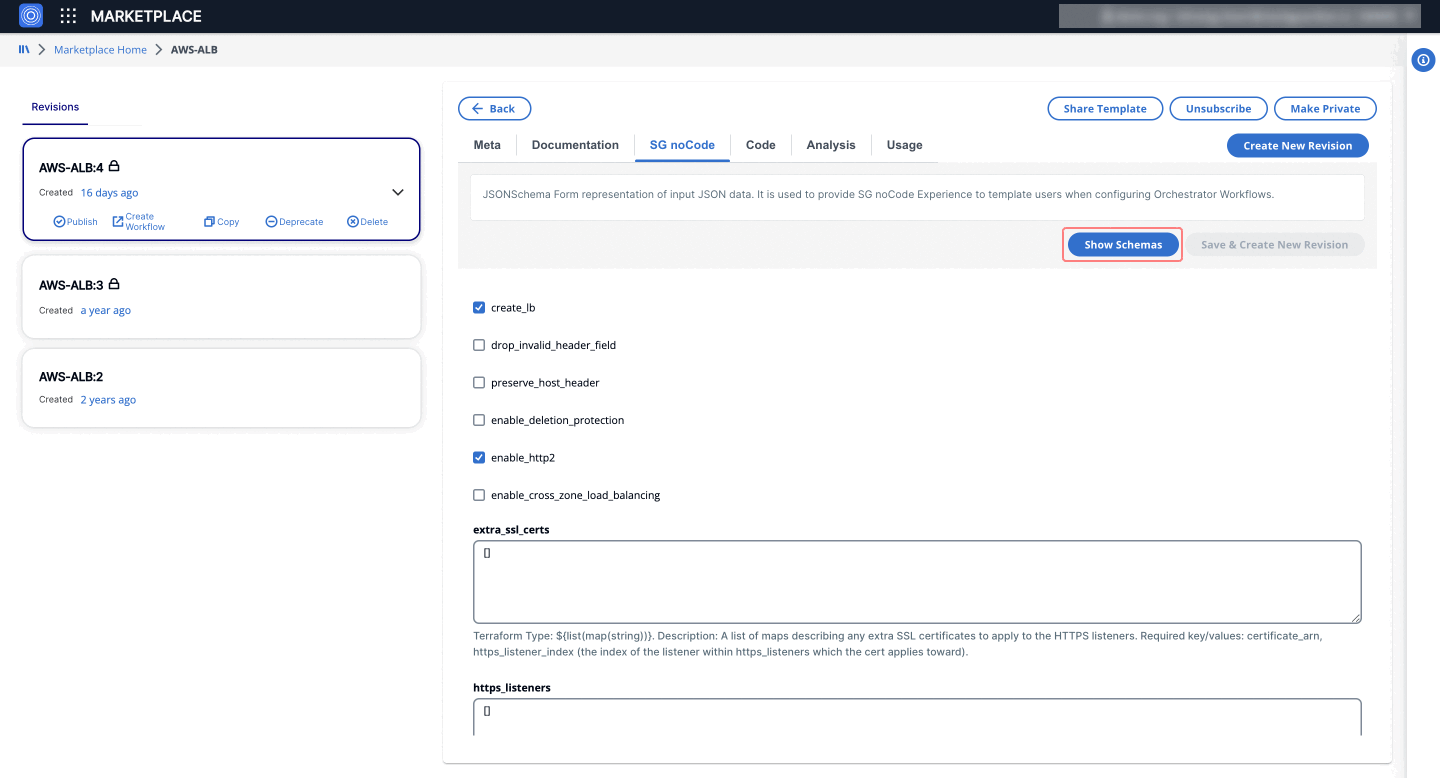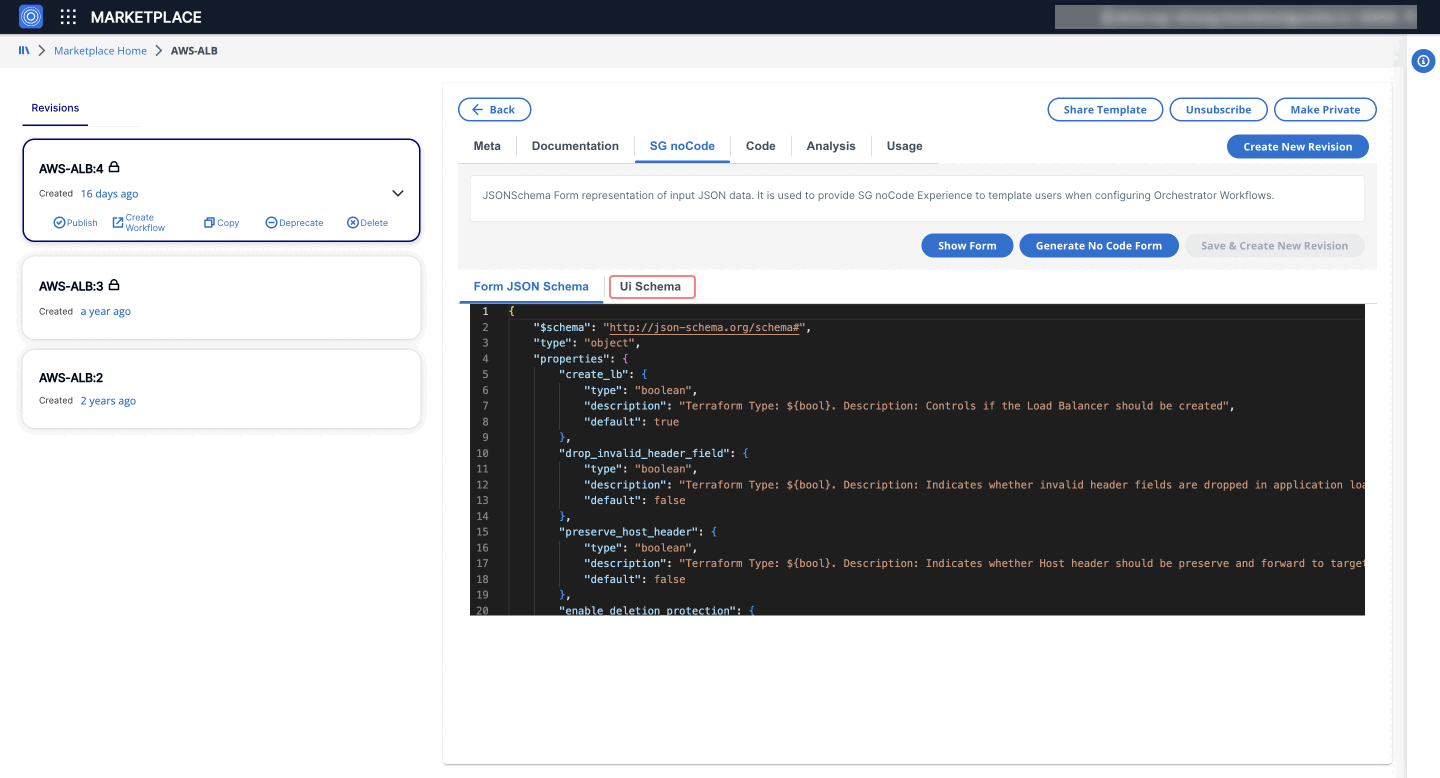
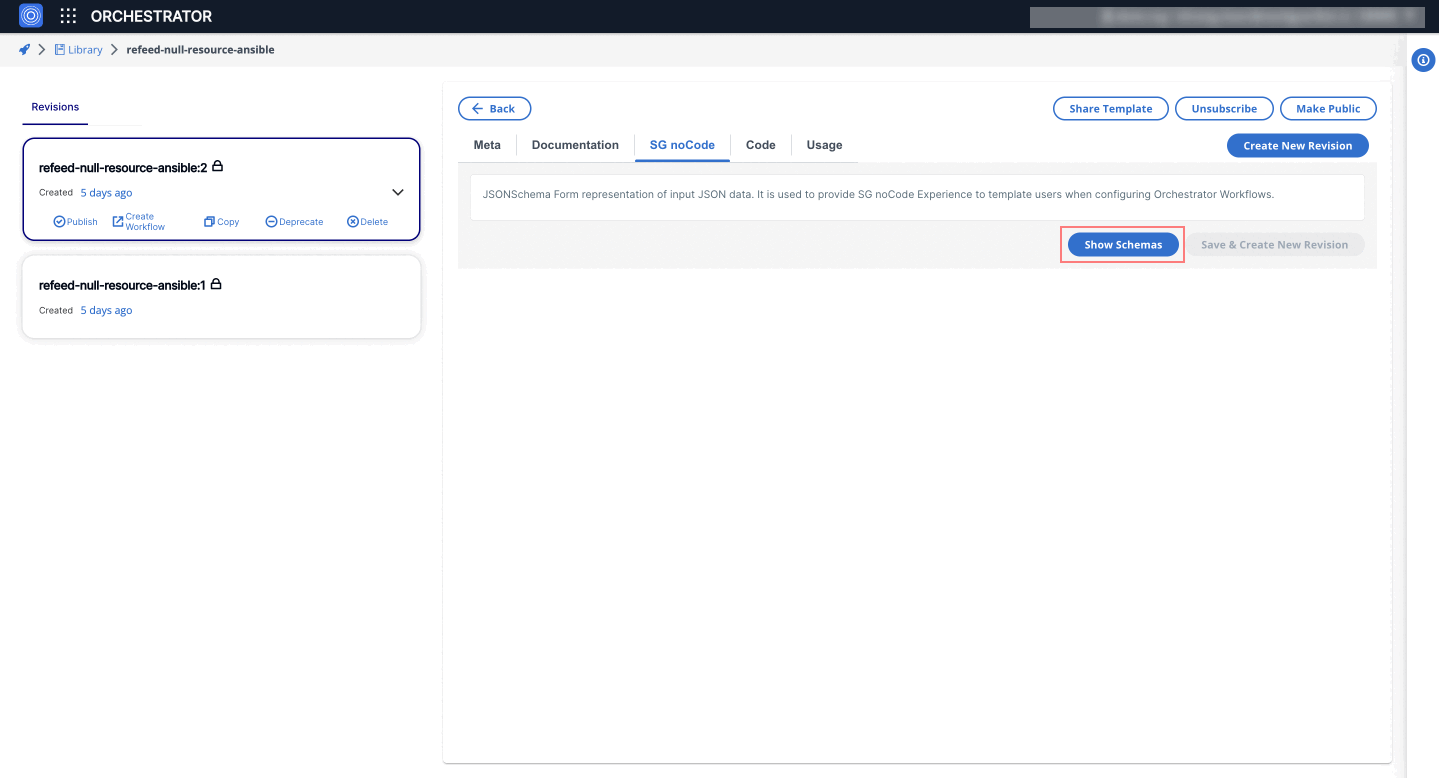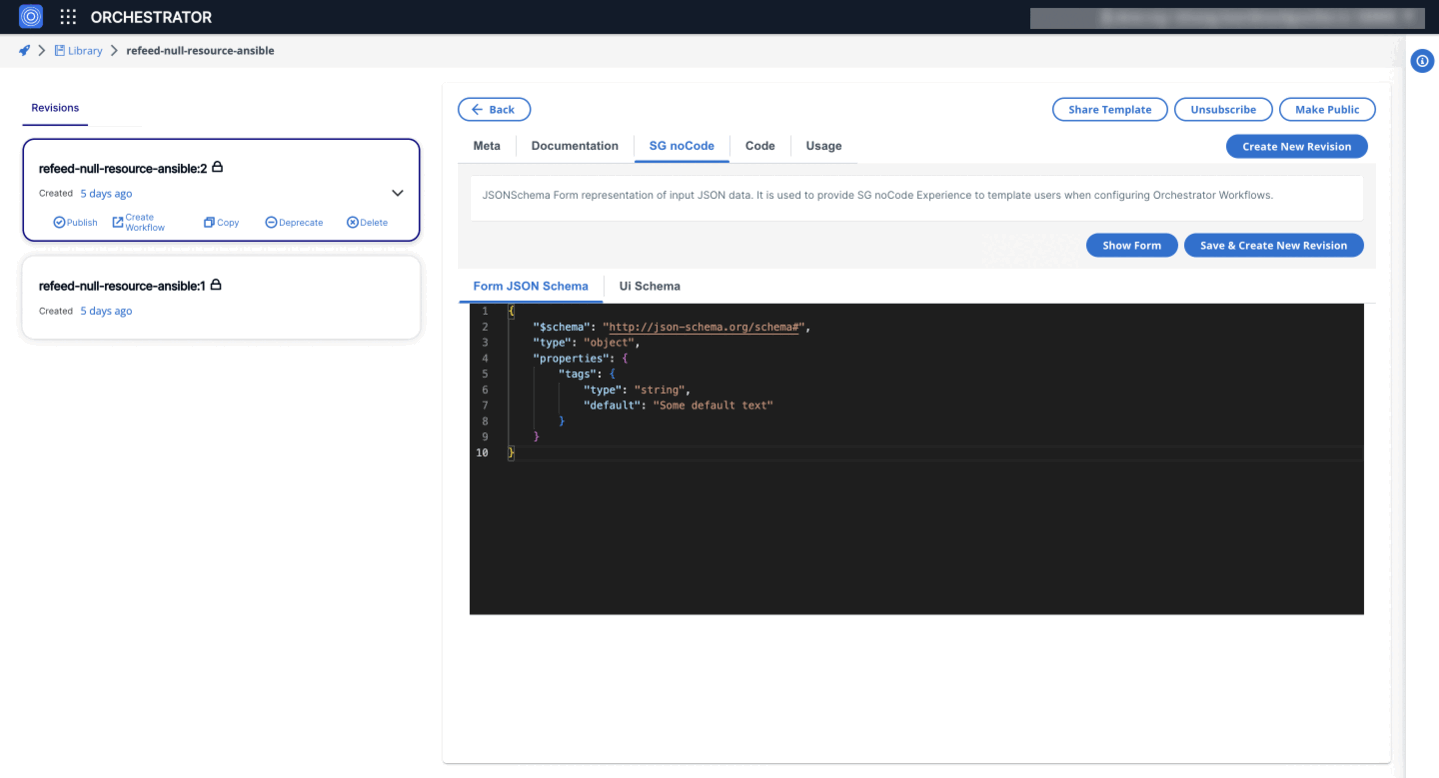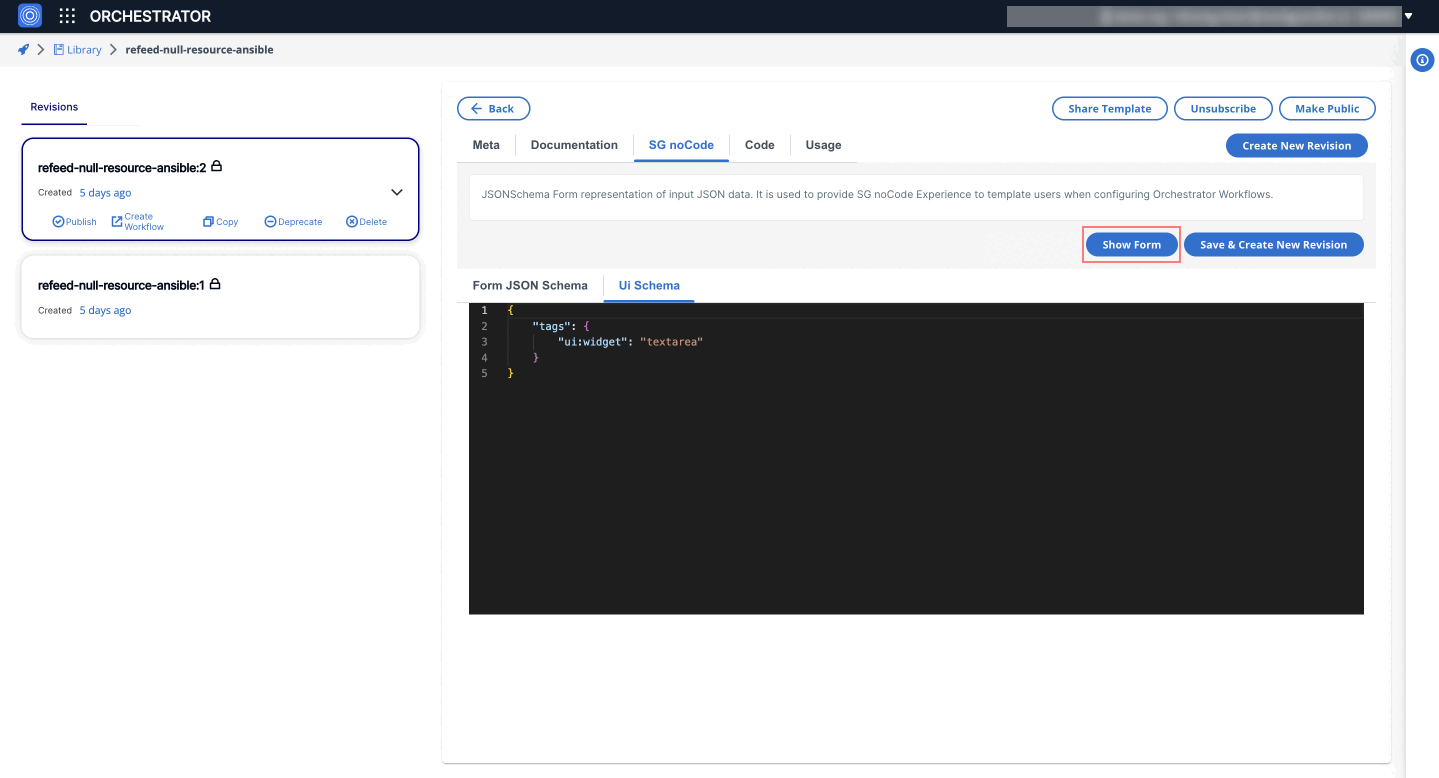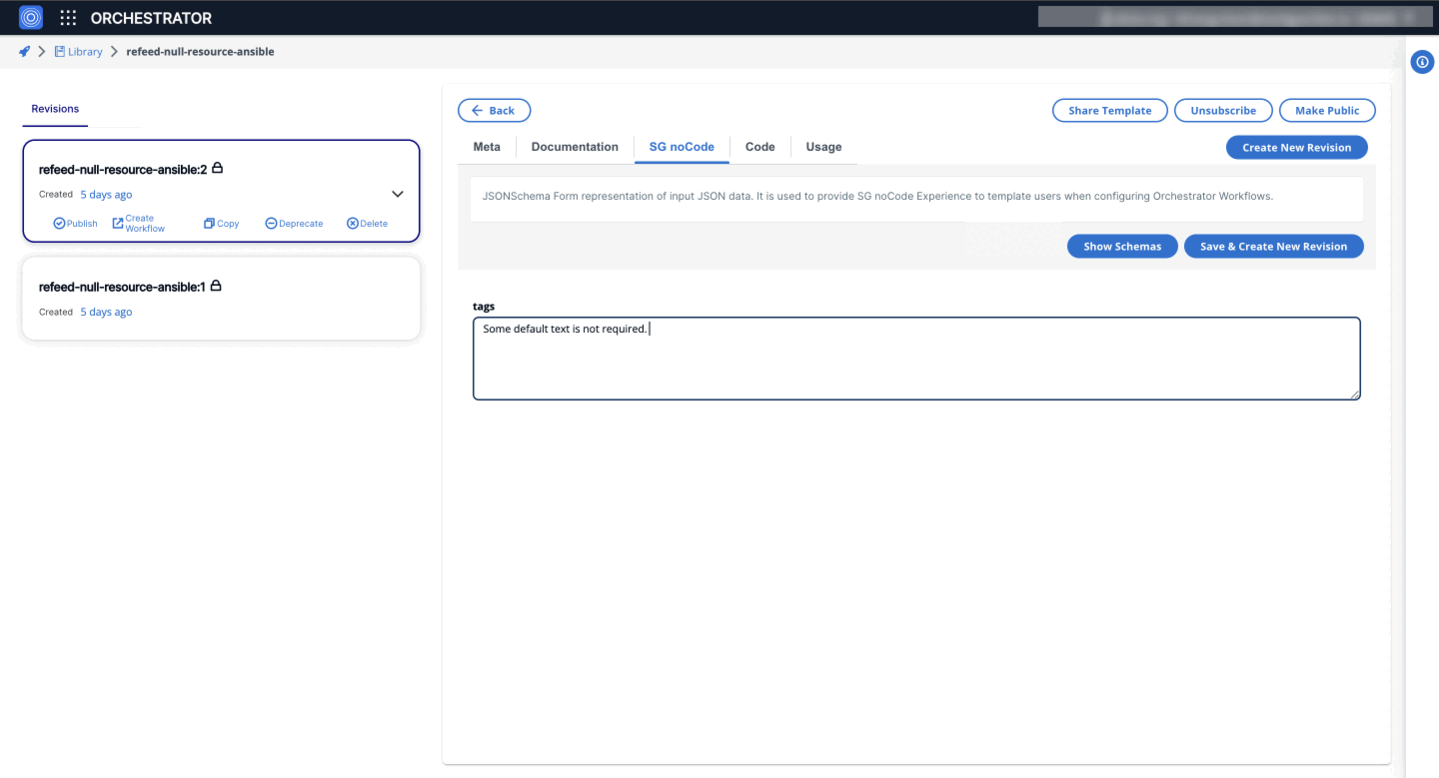
- SG noCode: This tab contains the JSONSchema Form representation of the input JSON data, used to provide the SG noCode experience for template users.
- Click on “Show Schema” to enable the Form JSON Schema.
JSON Schema Example
Below is an example of a JSON Schema defining properties, types, descriptions, and default values. Accepted types include "array", "boolean", "integer", "null", "number", "object", and "string".
{
"$schema": "http://json-schema.org/schema#",
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"enable_autoscaling": {
"type": "boolean",
"description": "Controls if autoscaling should be enabled for the deployment",
"default": true
},
"max_replicas": {
"type": "integer",
"description": "Maximum number of replicas for the autoscaling group",
"default": 10
},
"log_level": {
"type": "string",
"description": "Specifies the log level for the application (e.g., DEBUG, INFO, WARN, ERROR)",
"default": "INFO"
}
},
"required": ["enable_autoscaling", "max_replicas"]
}
Custom UI Widgets
Apart from the types mentioned above, we introduced custom UI widgets. The following custom UI widgets enhance the user experience by providing more flexibility and functionality in form creation.
1. Textarea Widget
Allows users to input multiline text, making it suitable for fields requiring extensive text entries, such as JSON objects.
- Form GUI
- Form JSON Schema
- UI Schema
{
"$schema": "http://json-schema.org/schema#",
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"tags": {
"type": "string",
"default": "Some default text"
}
}
}
{
"tags": {
"ui:widget": "textarea"
}
}
2. MultiSelectWidget
Enables users to select multiple options from a predefined list. This is useful for scenarios where multiple selections are needed.
- Form GUI
- Form JSON Schema
- UI Schema
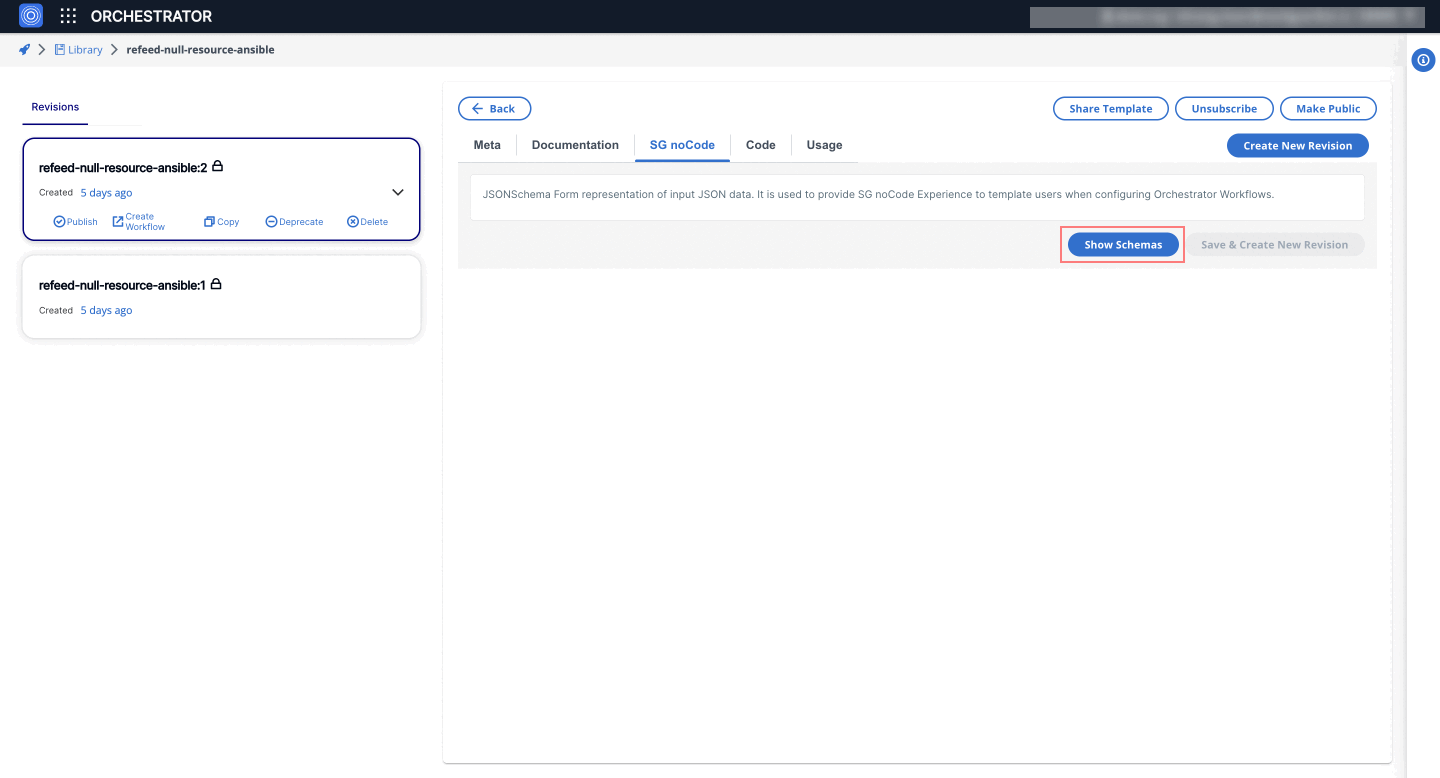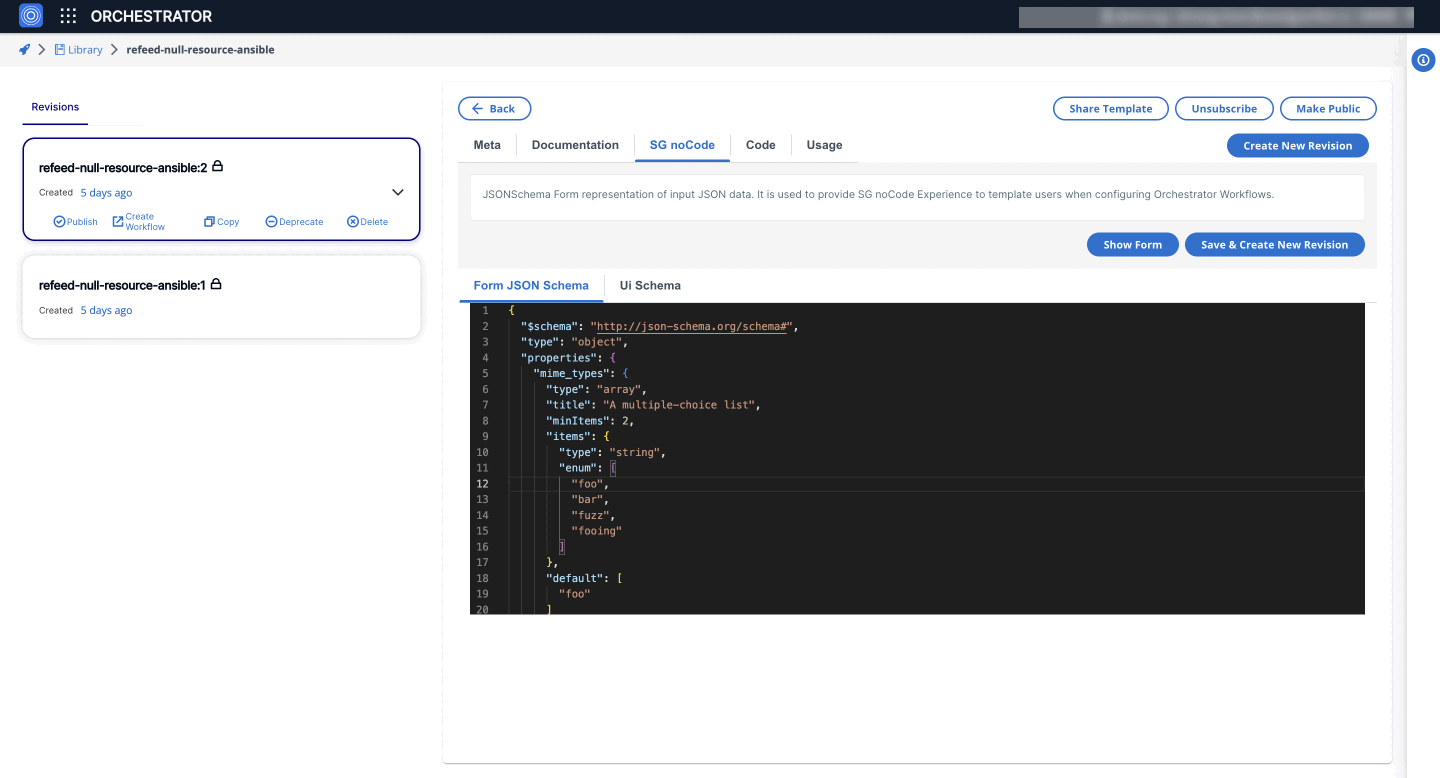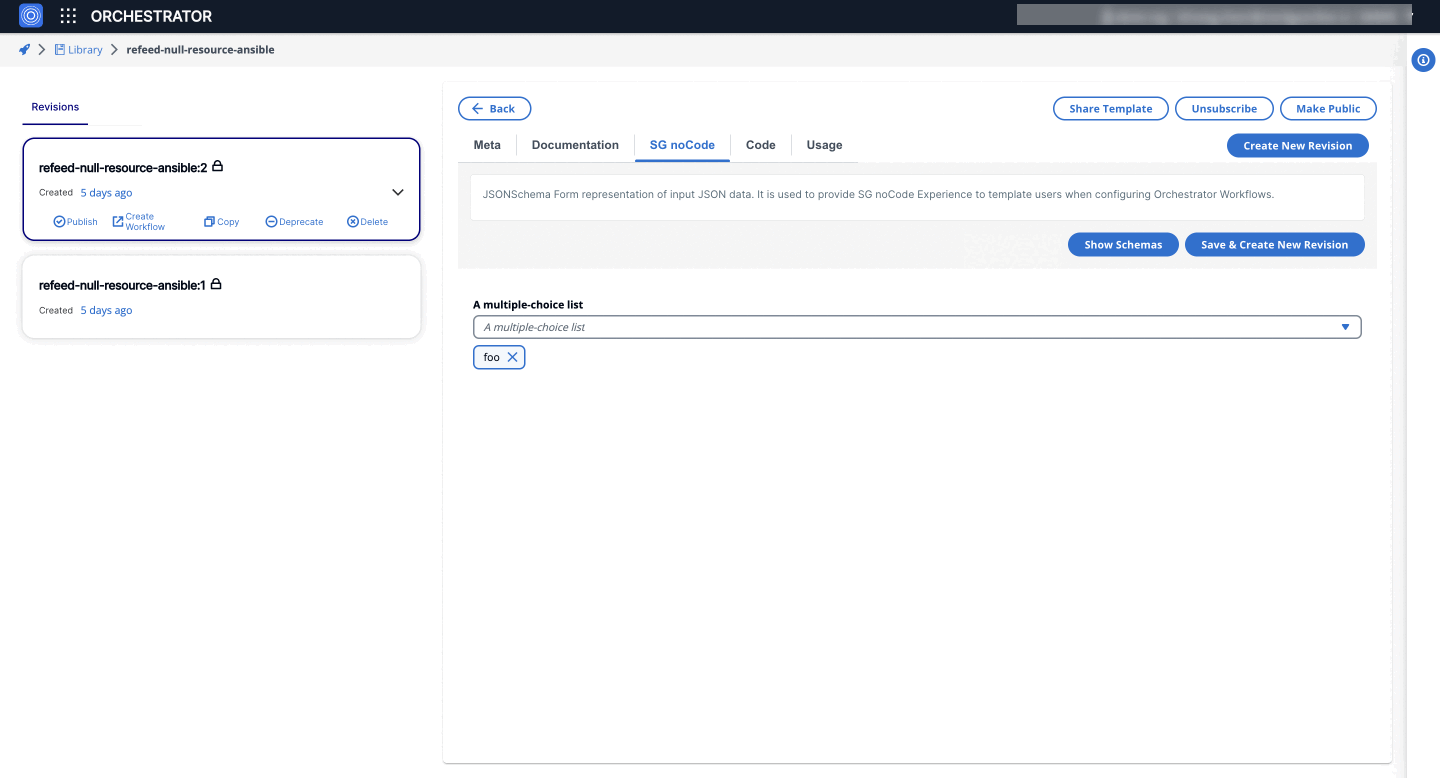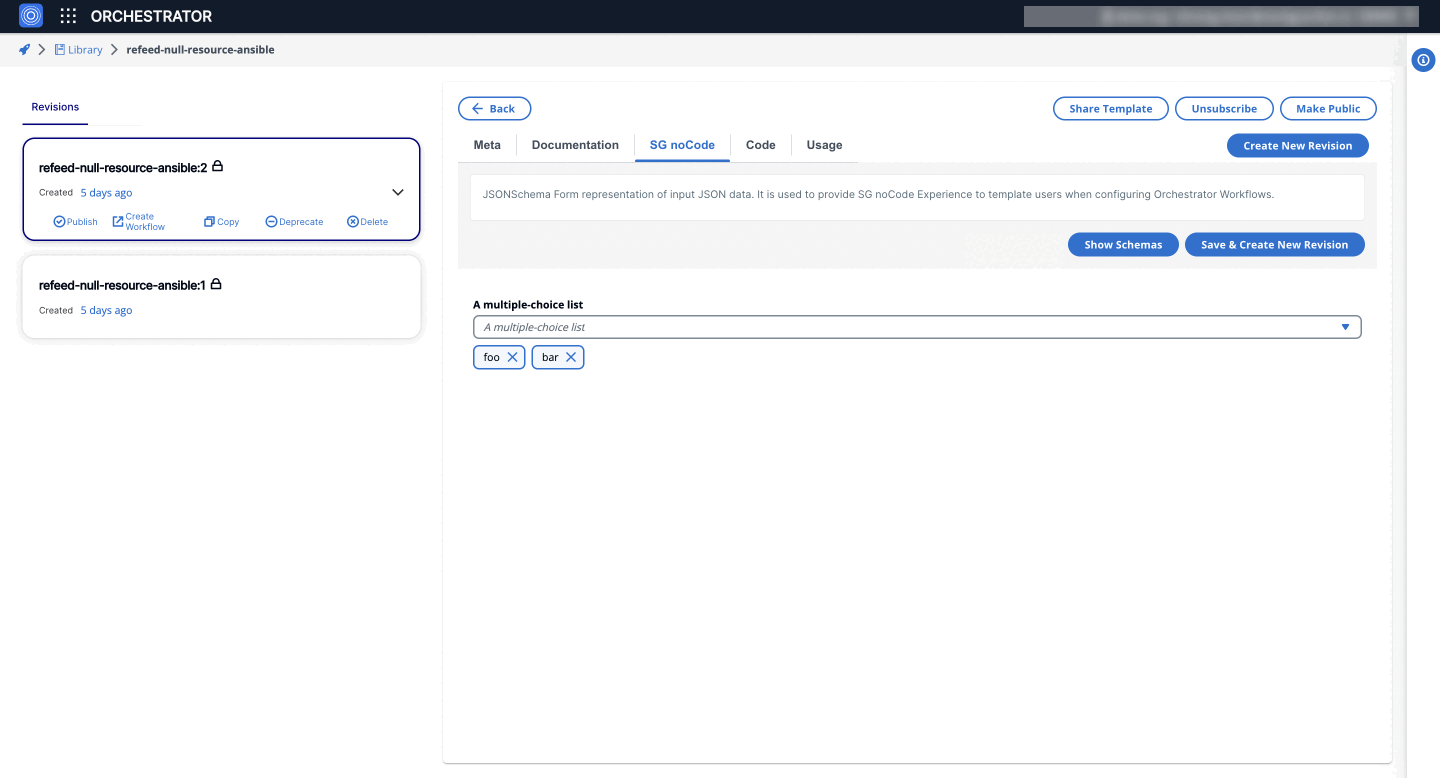
{
"$schema": "http://json-schema.org/schema#",
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"mime_types": {
"type": "array",
"title": "A multiple-choice list",
"minItems": 2,
"items": {
"type": "string",
"enum": [
"foo",
"bar",
"fuzz",
"fooing"
]
},
"default": [
"foo"
]
}
}
}
{
"mime_types": {
"ui:widget": "MultiSelectWidget"
}
}
3. SelectWidget
Allows users to select a single option from a dropdown list. It is similar to the default Select field in RJSF but offers additional customization.
- Form GUI
- Form JSON Schema
- UI Schema
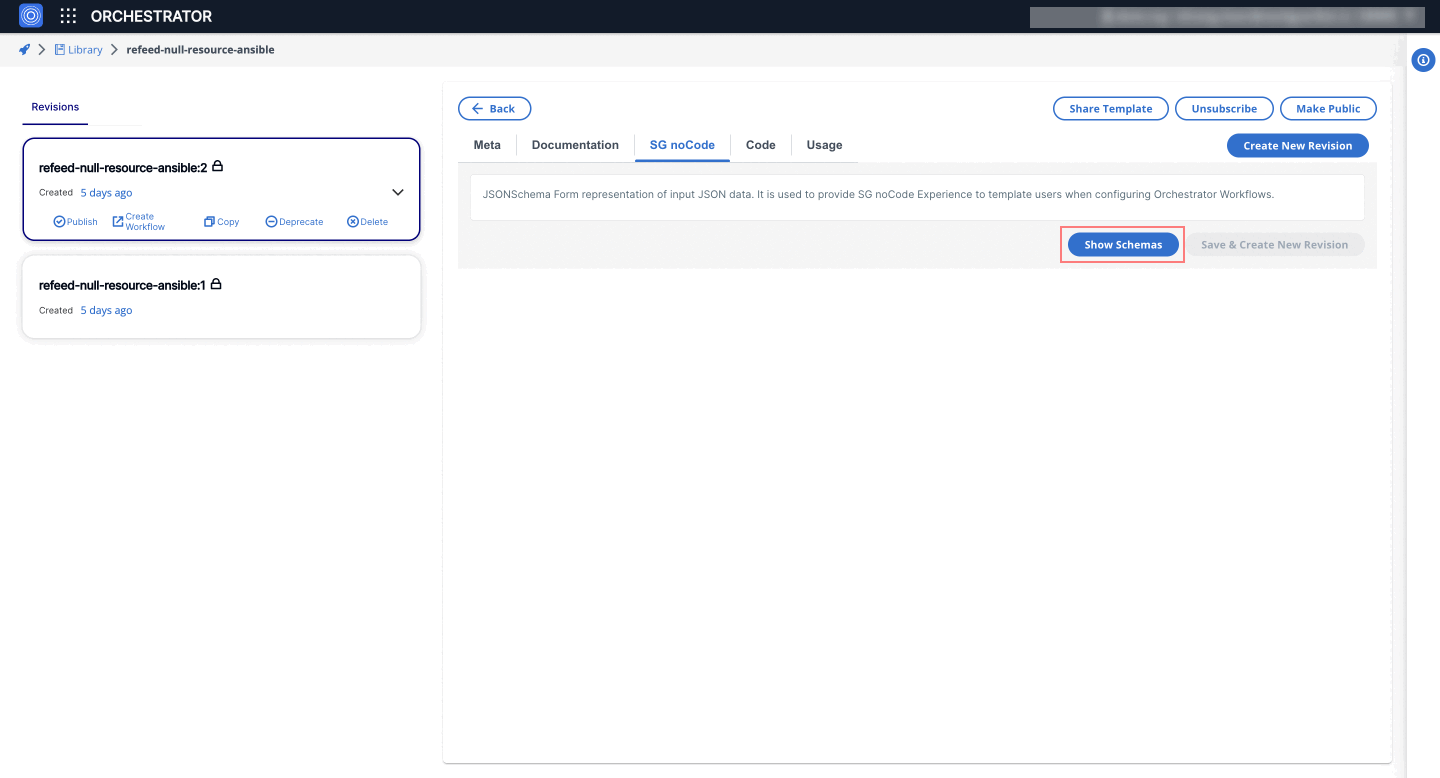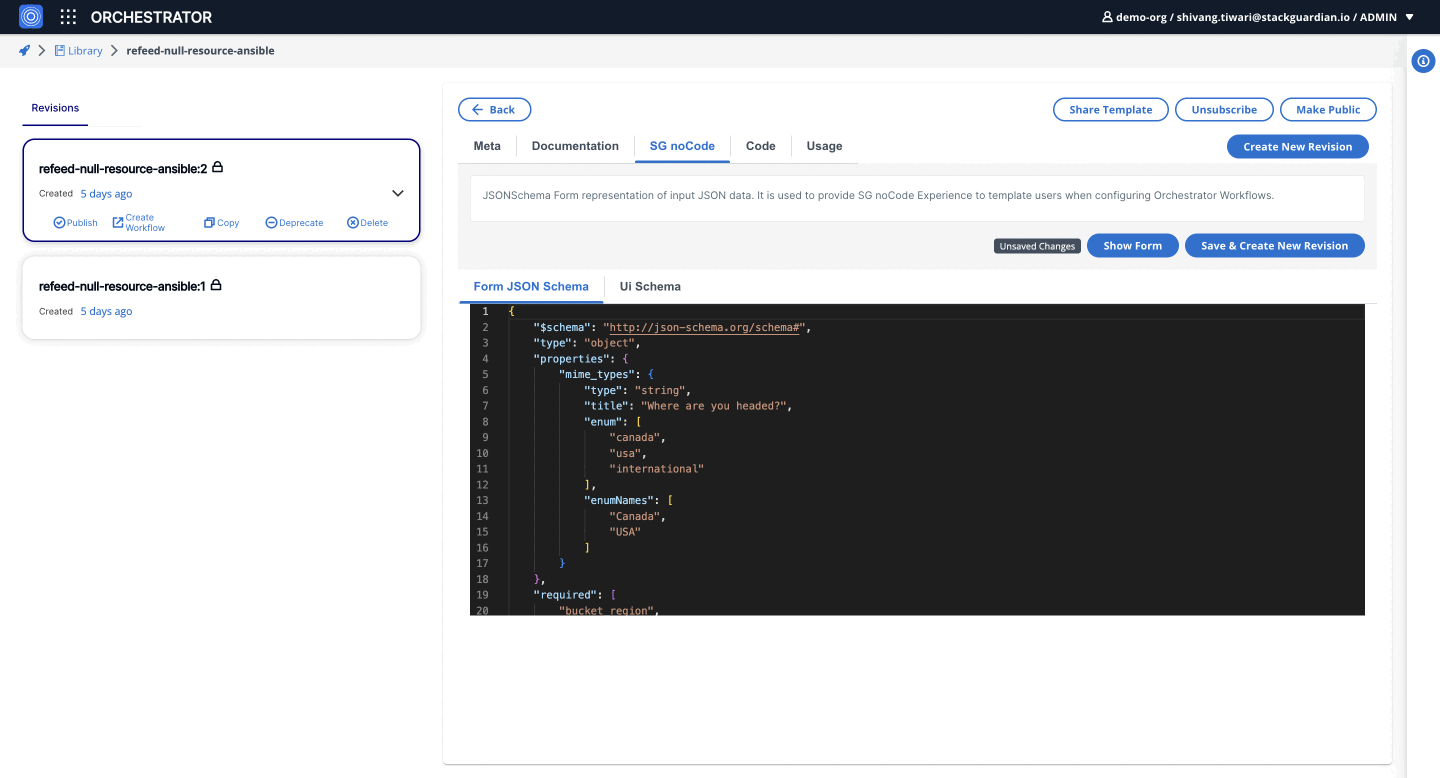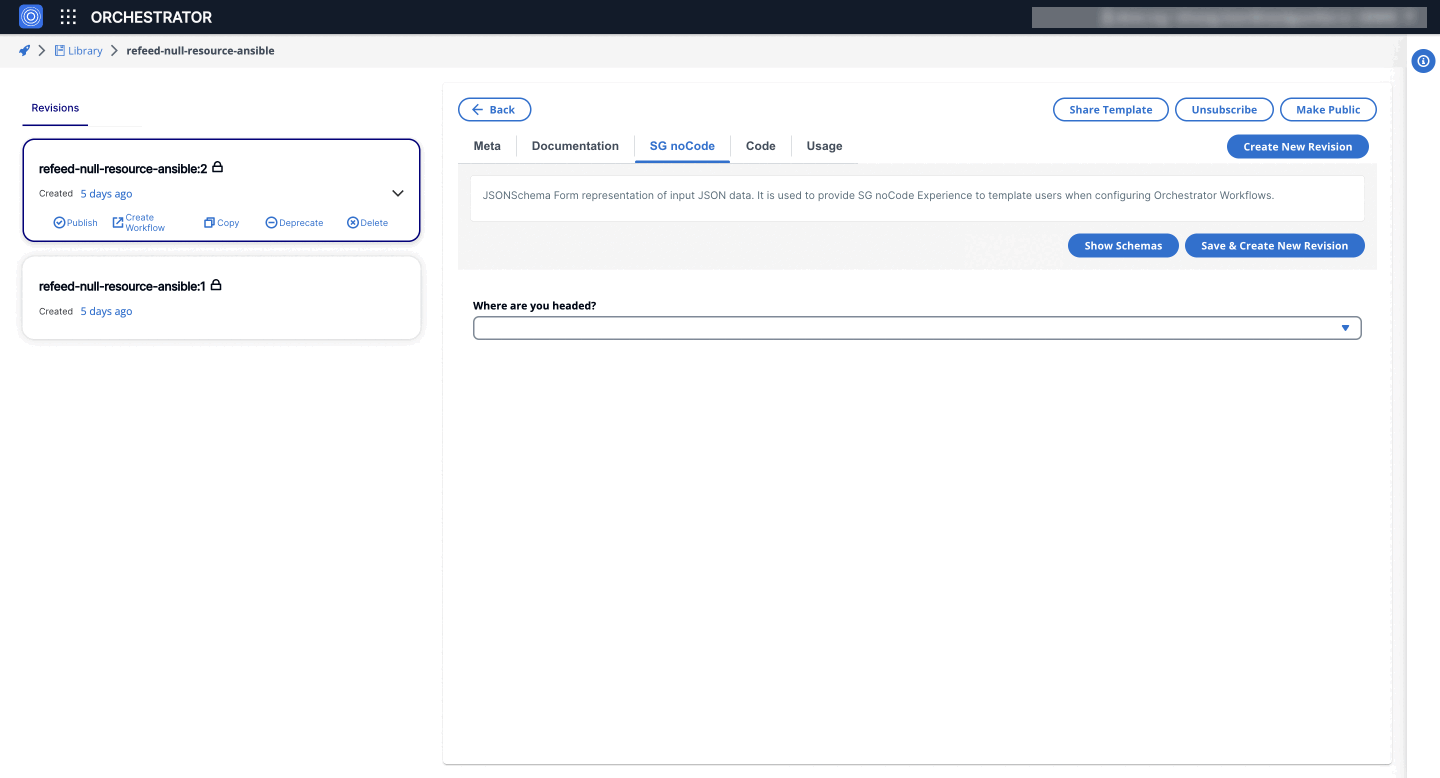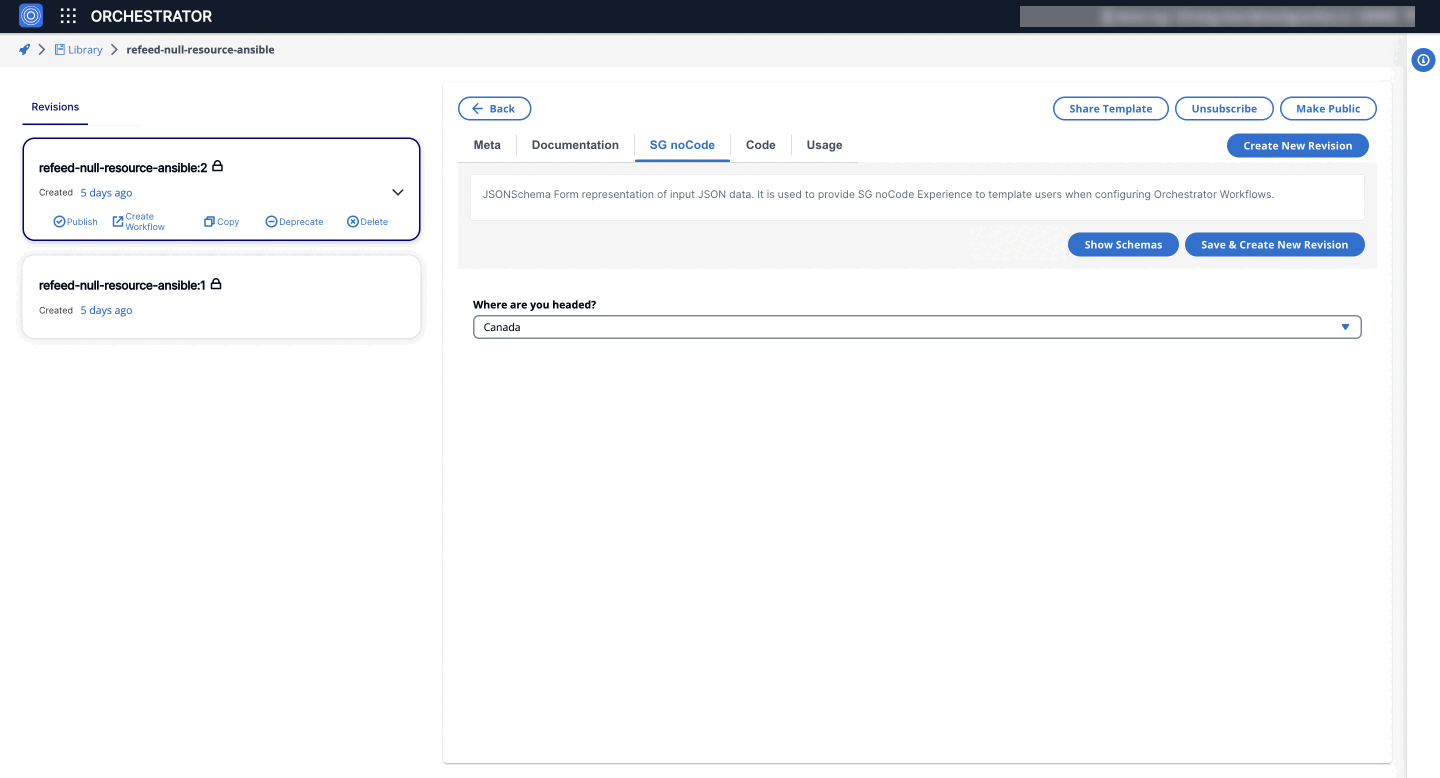
{
"$schema": "http://json-schema.org/schema#",
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"mime_types": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Where are you headed?",
"enum": [
"canada",
"usa",
"international"
],
"enumNames": [
"Canada",
"USA"
]
}
},
"required": [
"bucket_region",
"mime_types"
]
}
{
"mime_types": {
"ui:widget": "SelectWidget"
}
}
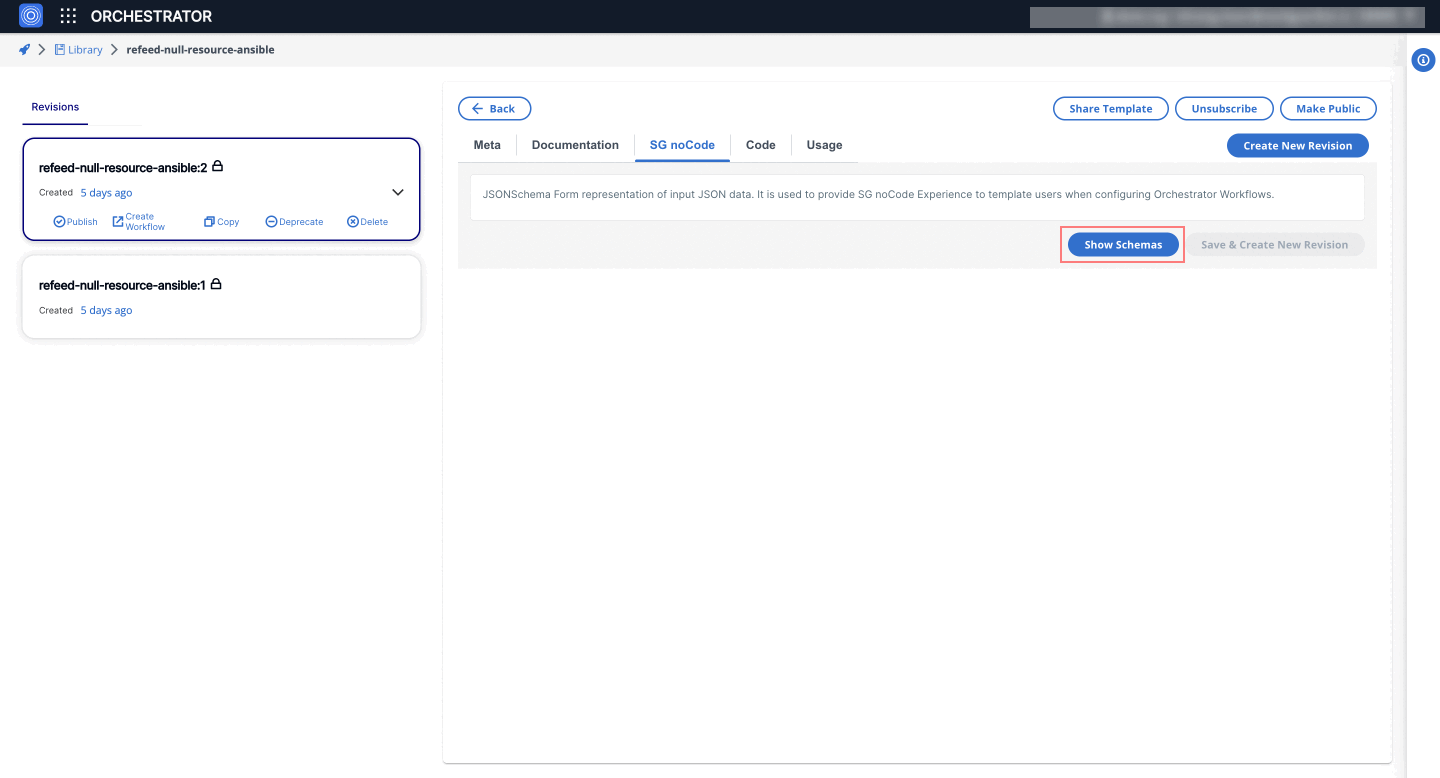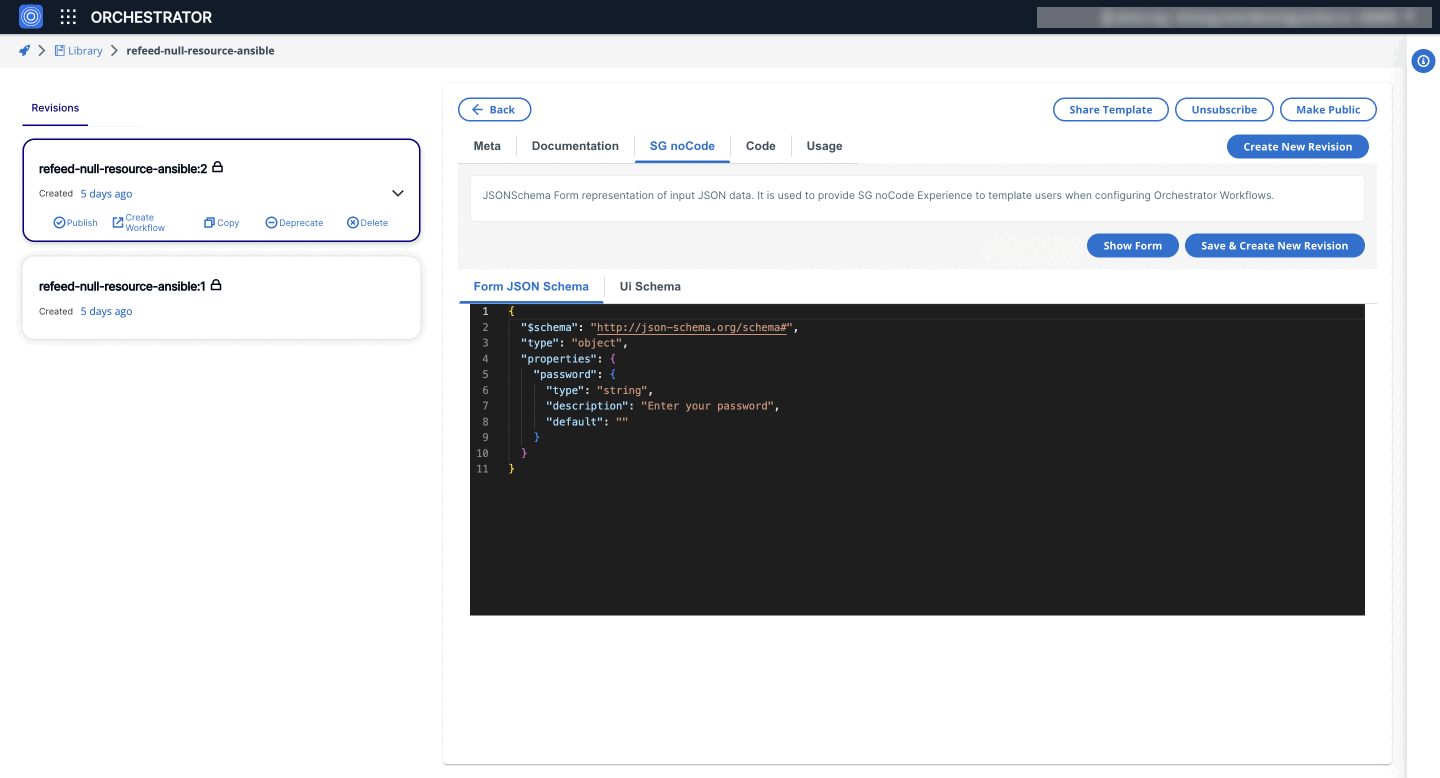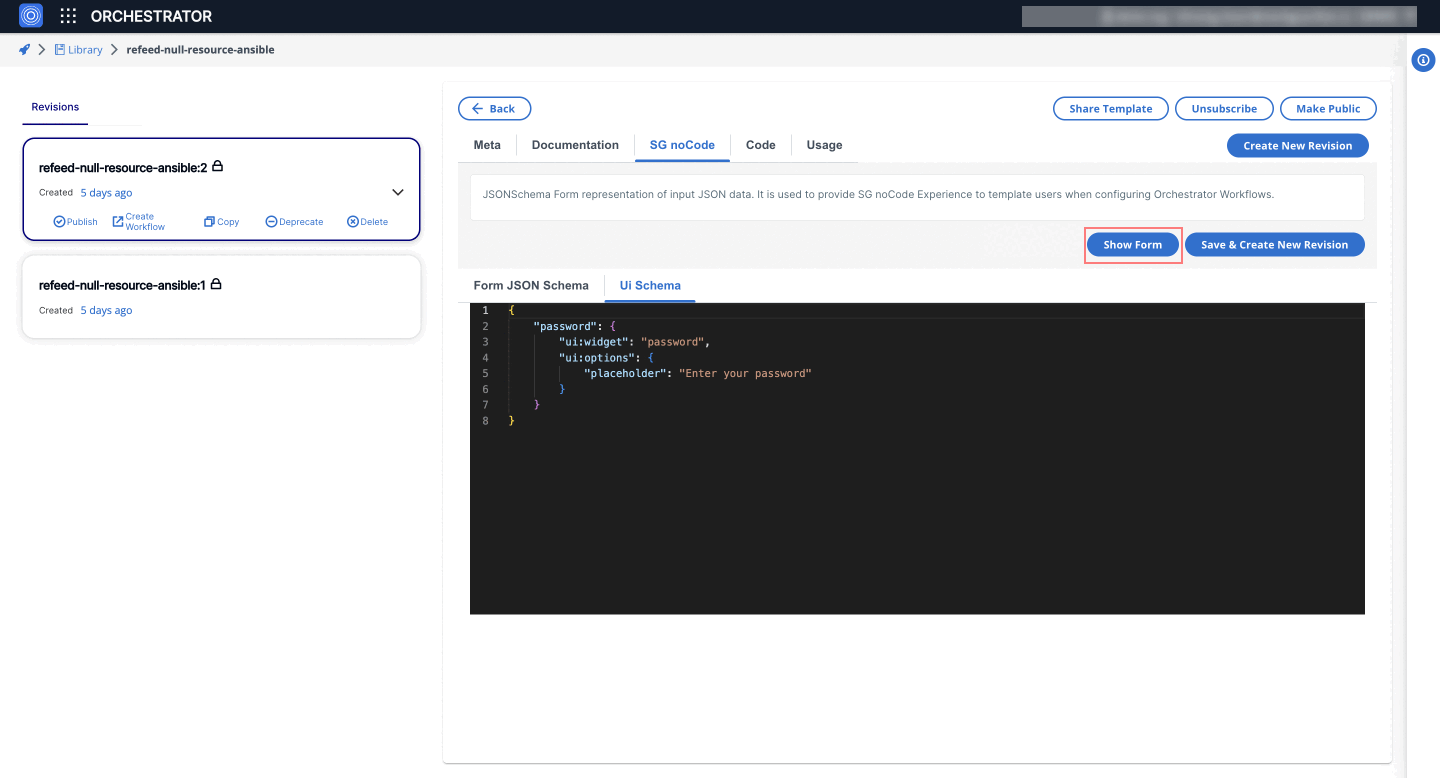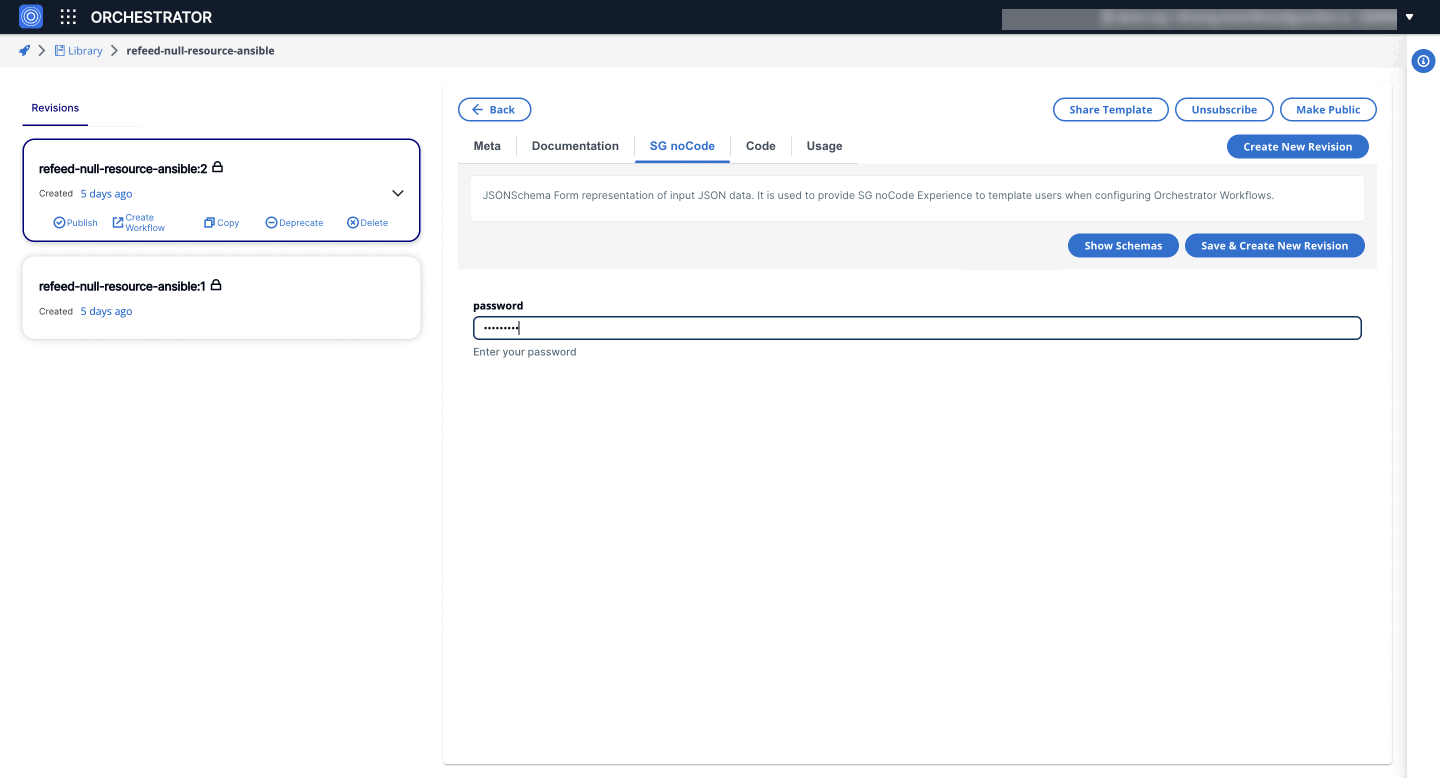
4. Password Widget
The password widget renders a string field with password type functionality, masking the input.
- Form GUI
- Form JSON Schema
- UI Schema
{
"password": {
"type": "string",
"description": "Enter your password",
"default": ""
}
}
{
"password": {
"ui:widget": "password",
"ui:options": {
"placeholder": "Enter your password"
}
}
}
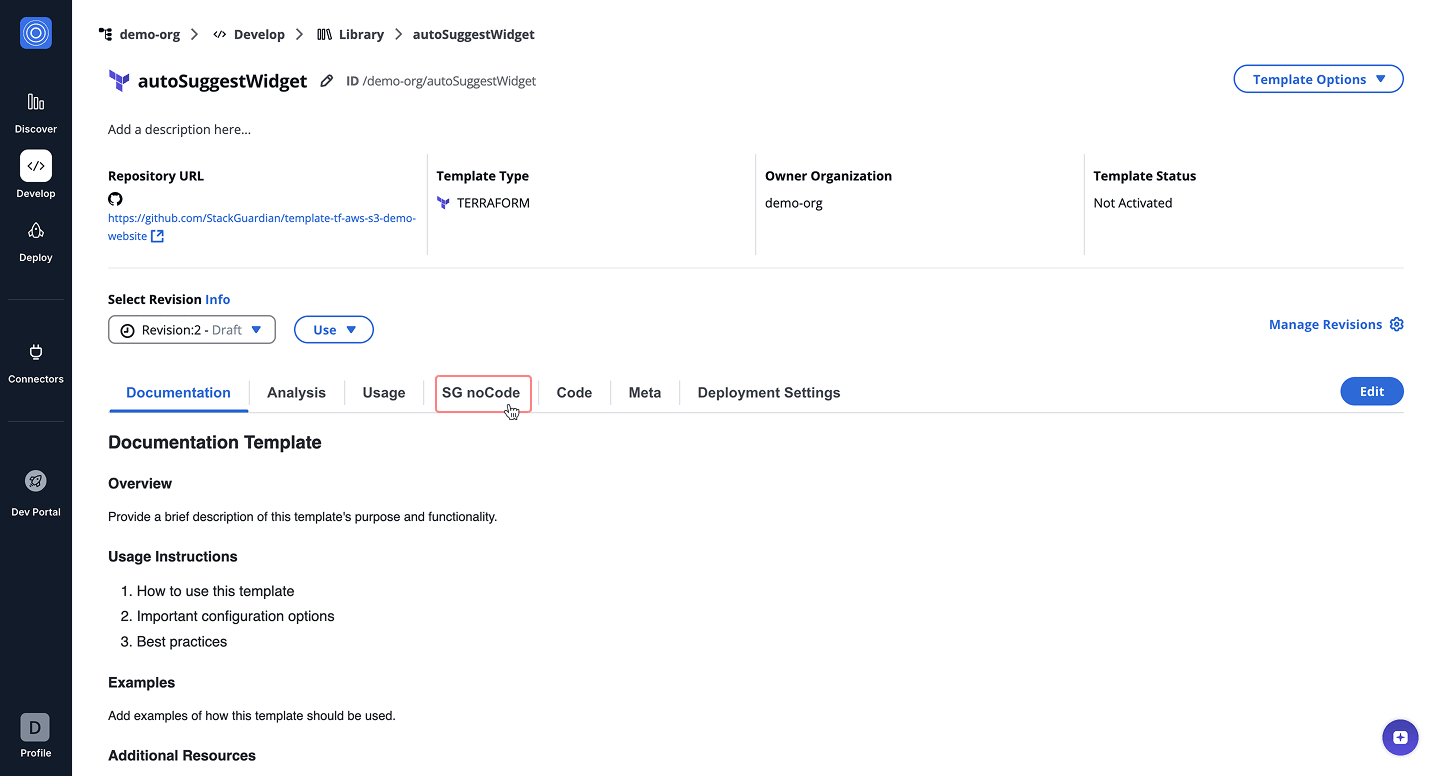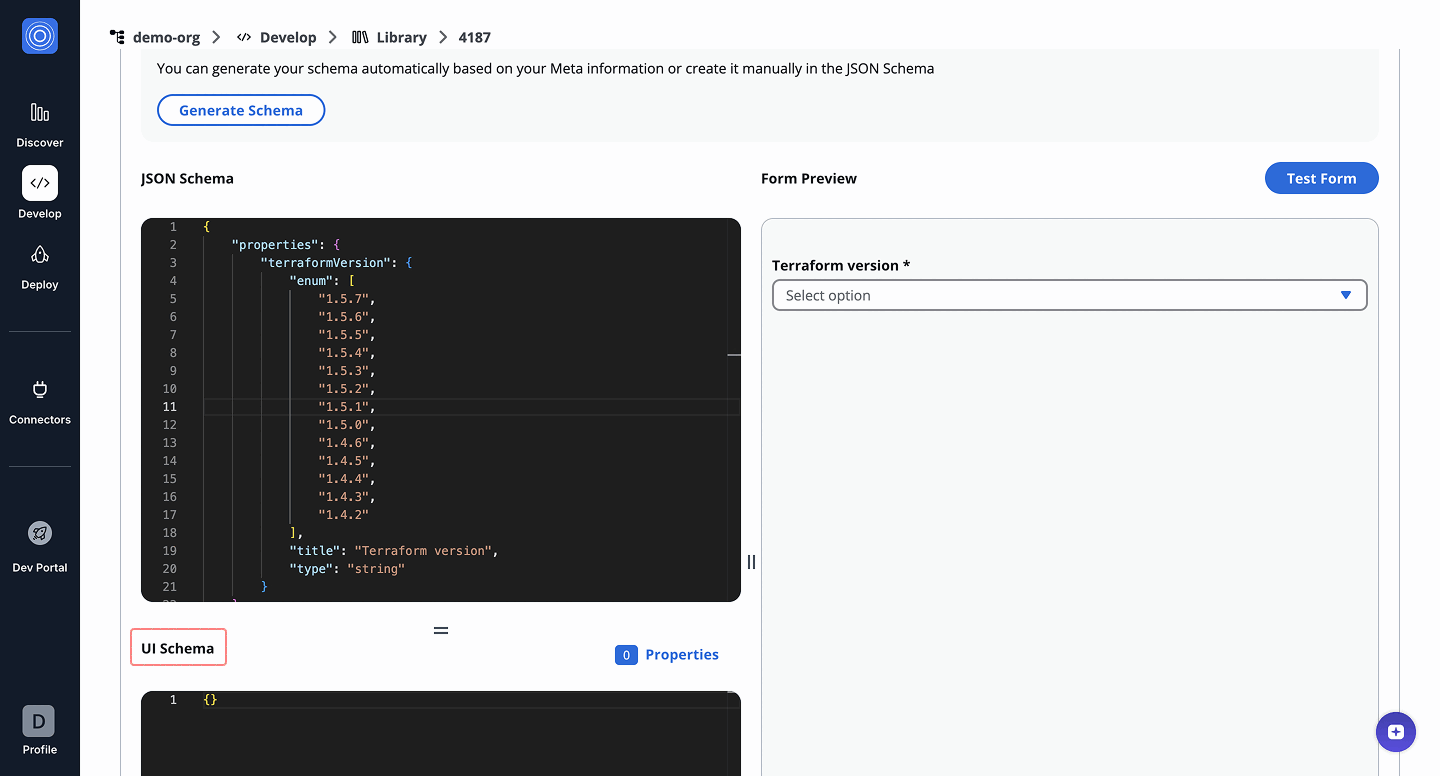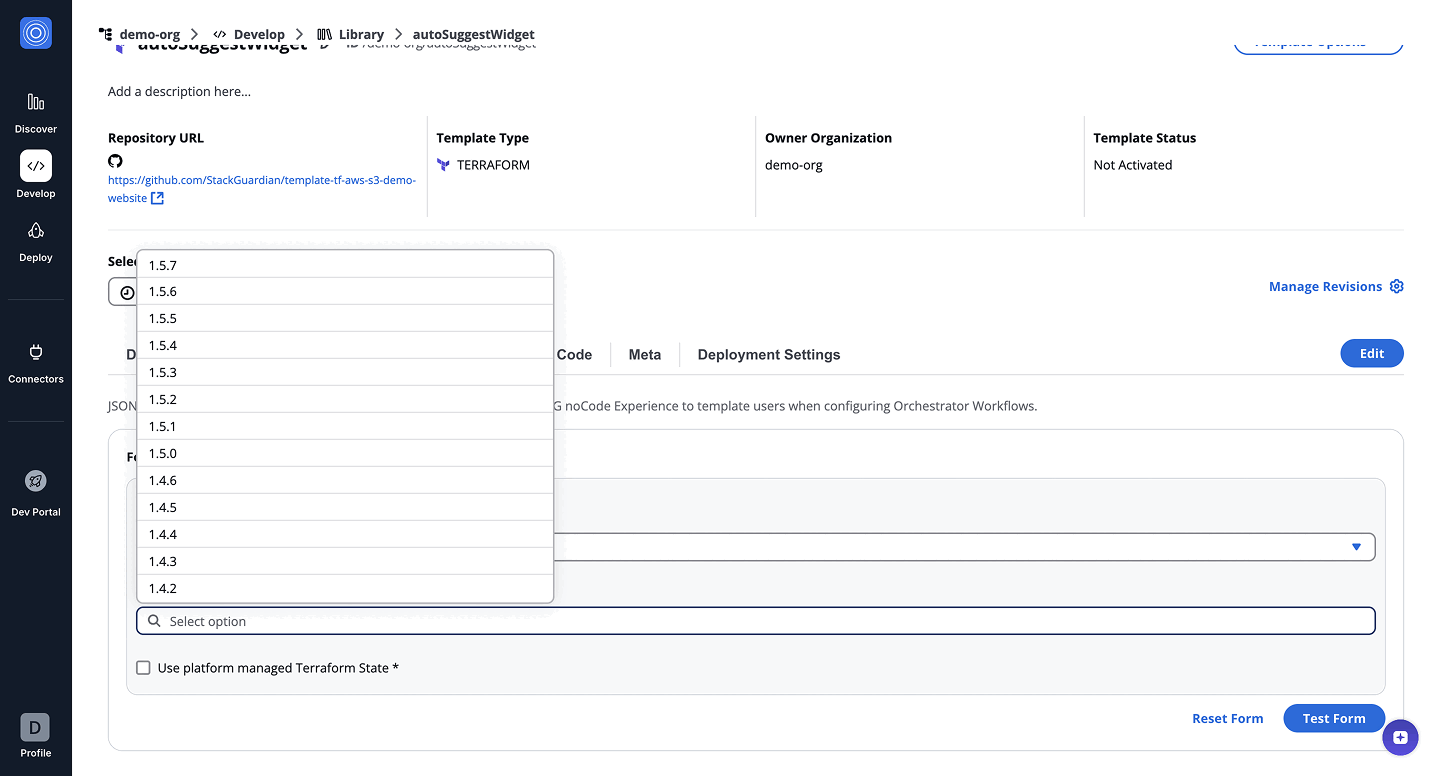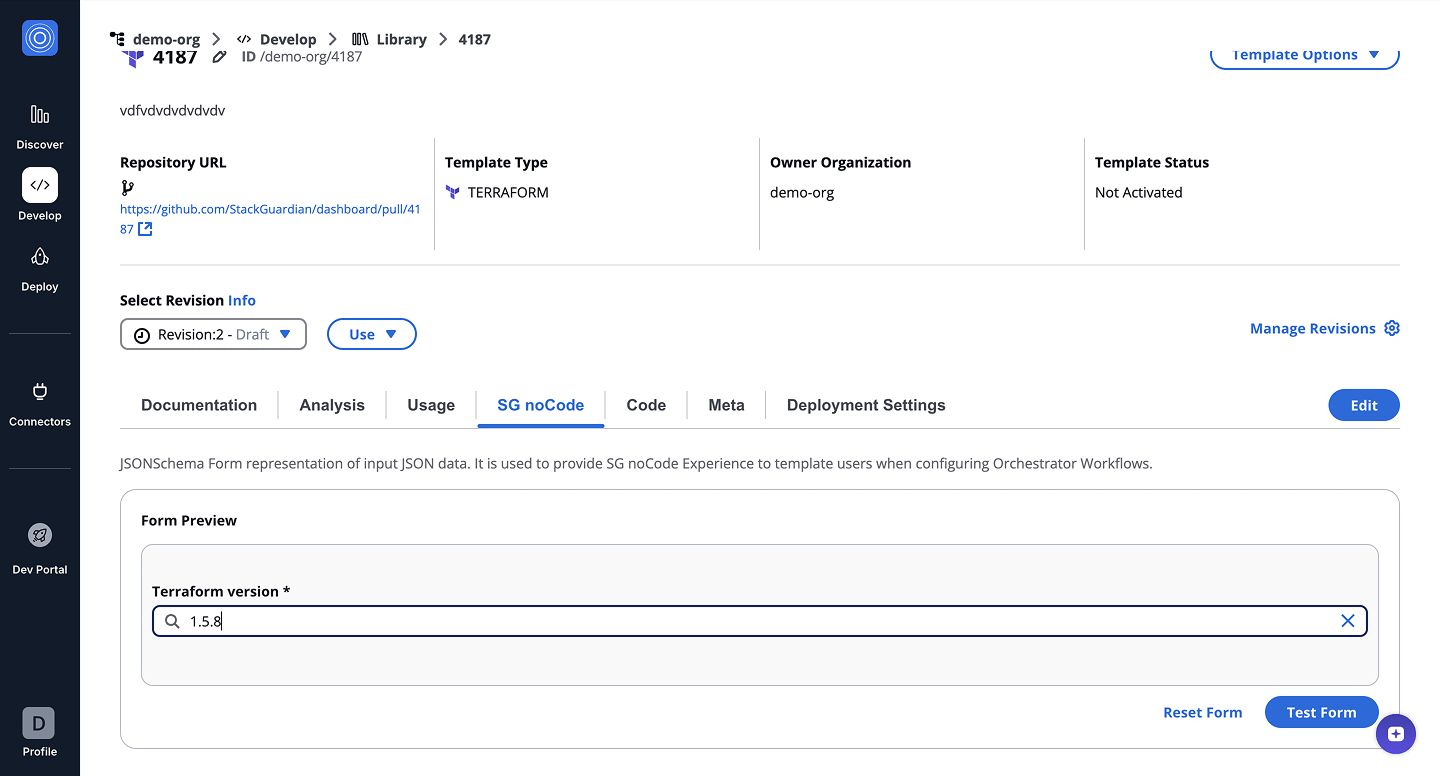
5. CustomAutoSuggestWidget
The CustomAutoSuggest renders a string field with autocomplete, letting users pick from a list or enter a custom value and offering more flexibility than regular dropdowns.
- Form GUI
- Form JSON Schema
- UI Schema
{
"properties": {
"terraformVersion": {
"enum": [
"1.5.7",
"1.5.6",
"1.5.5",
"1.5.4",
"1.5.3",
"1.5.2",
"1.5.1",
"1.5.0",
"1.4.6",
"1.4.5",
"1.4.4",
"1.4.3",
"1.4.2"
],
"title": "Terraform version",
"type": "string"
}
},
"required": [
"terraformVersion"
],
"title": "",
"type": "object"
}
{
"terraformVersion": {
"ui:widget": "CustomAutoSuggestWidget"
}
}
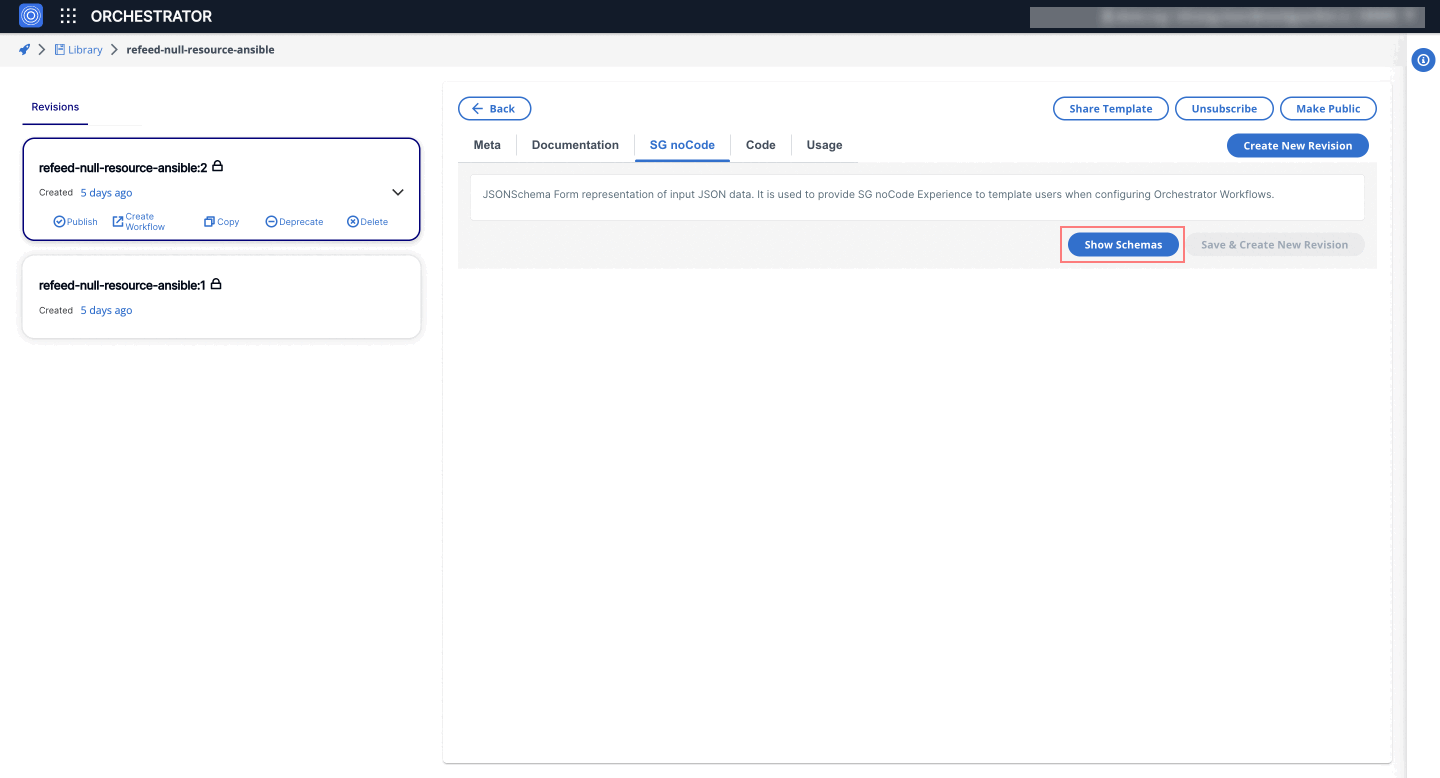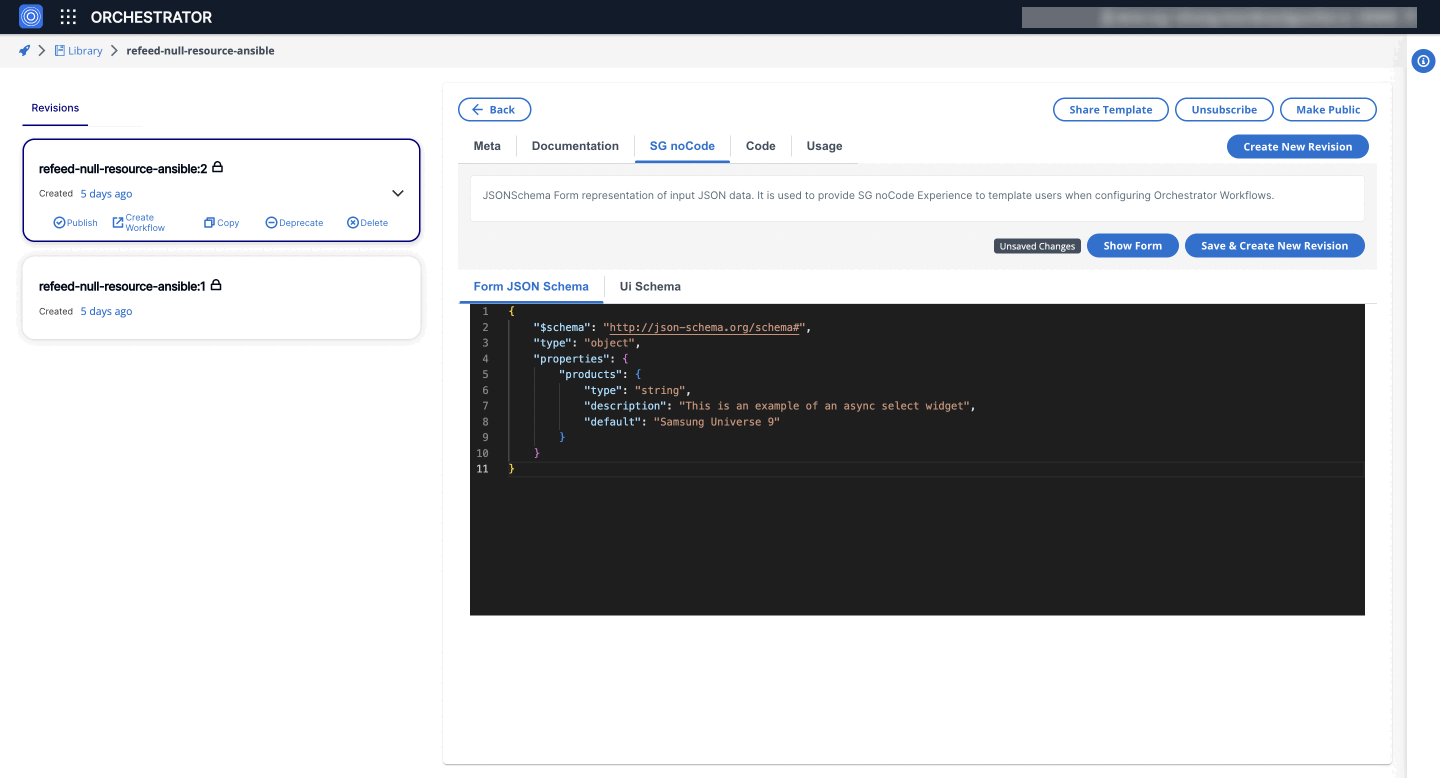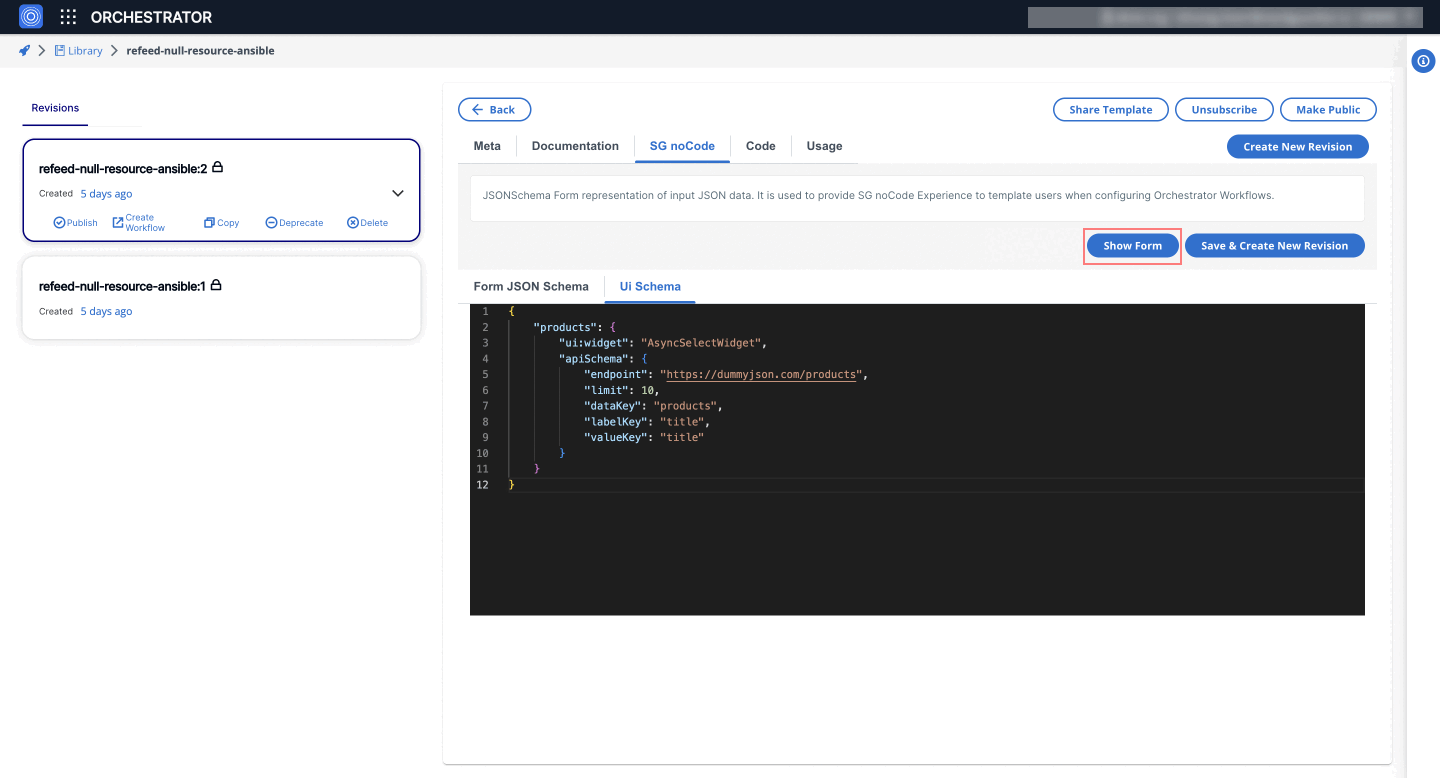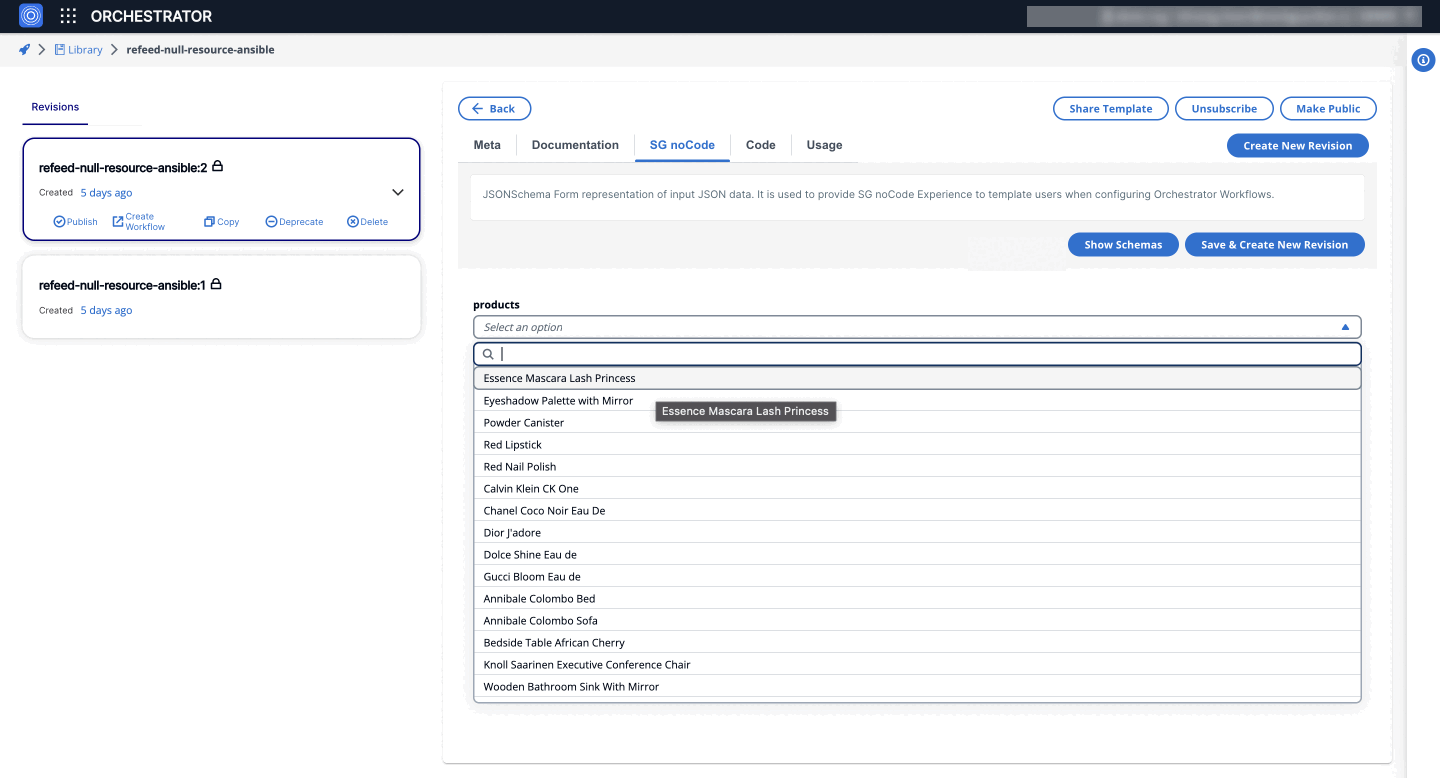
6. AsyncSelectWidget
The AsyncSelectWidget is a dynamic select component that makes an API call to fetch options. This is useful for scenarios where the options are not static and need to be retrieved from a server.
- Form GUI
- Form JSON Schema
- UI Schema
{
"$schema": "http://json-schema.org/schema#",
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"products": {
"type": "string",
"description": "This is an example of an async select widget",
"default": "Samsung Universe 9"
}
}
}
{
"products": {
"ui:widget": "AsyncSelectWidget",
"apiSchema": {
"endpoint": "https://dummyjson.com/products",
"limit": 10,
"dataKey": "products",
"labelKey": "title",
"valueKey": "title"
}
}
}
7. CustomCodeFrontendWidget
The CustomCodeFrontendWidget enables dynamic and context-aware customization of form fields in real-time, allowing users to fetch, process, and populate form data dynamically. Unlike the CustomCodeWidget, where the JavaScript code is executed in a backend Lambda environment, this widget executes the JavaScript directly in the user's browser.
This is useful for scenarios where users need to dynamically adjust the form fields based on real-time data, such as fetching workflow outputs from the StackGuardian API.
The CustomCodeFrontendWidget does not make use of Cloud Connectors (Azure, AWS, GCP) to fetch data from Cloud Providers. For these use cases, the CustomCodeWidget should be used.
Key Features
- Dynamic Data Fetching: Fetch data from APIs or other sources in real-time.
- Custom JavaScript Support: Users can write custom JavaScript to handle data processing and form updates.
- Contextual Awareness: Leverages variables like
sg_contextfor details such asorg,wfgrp,stack, andwf.
How It Works
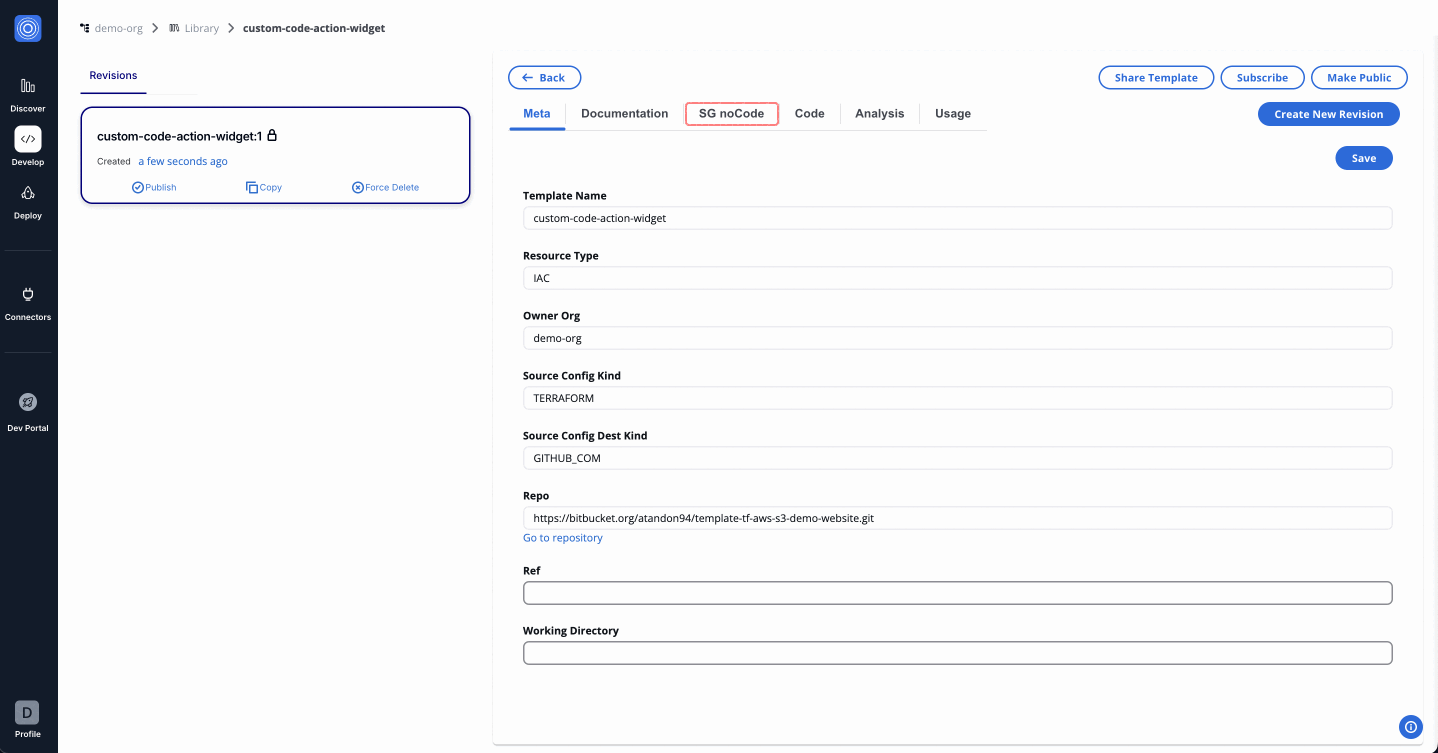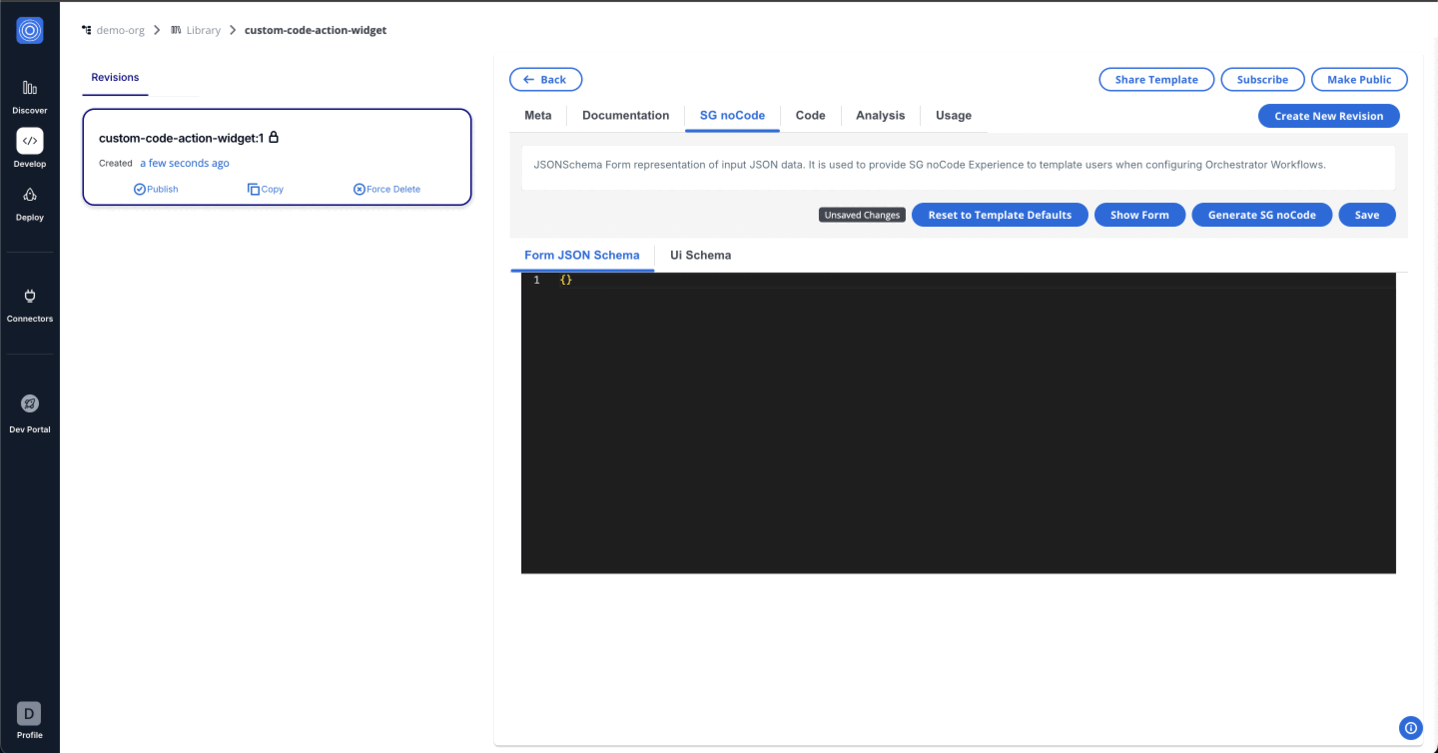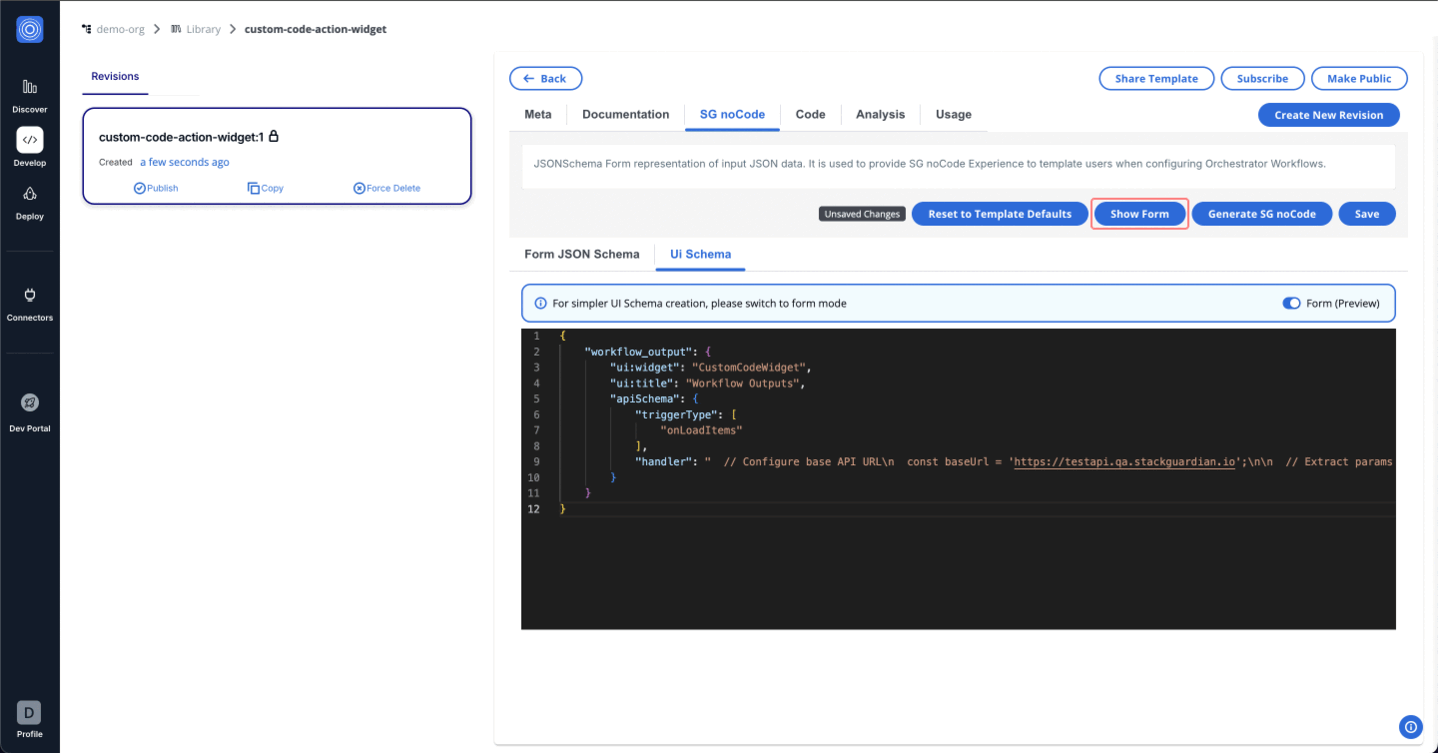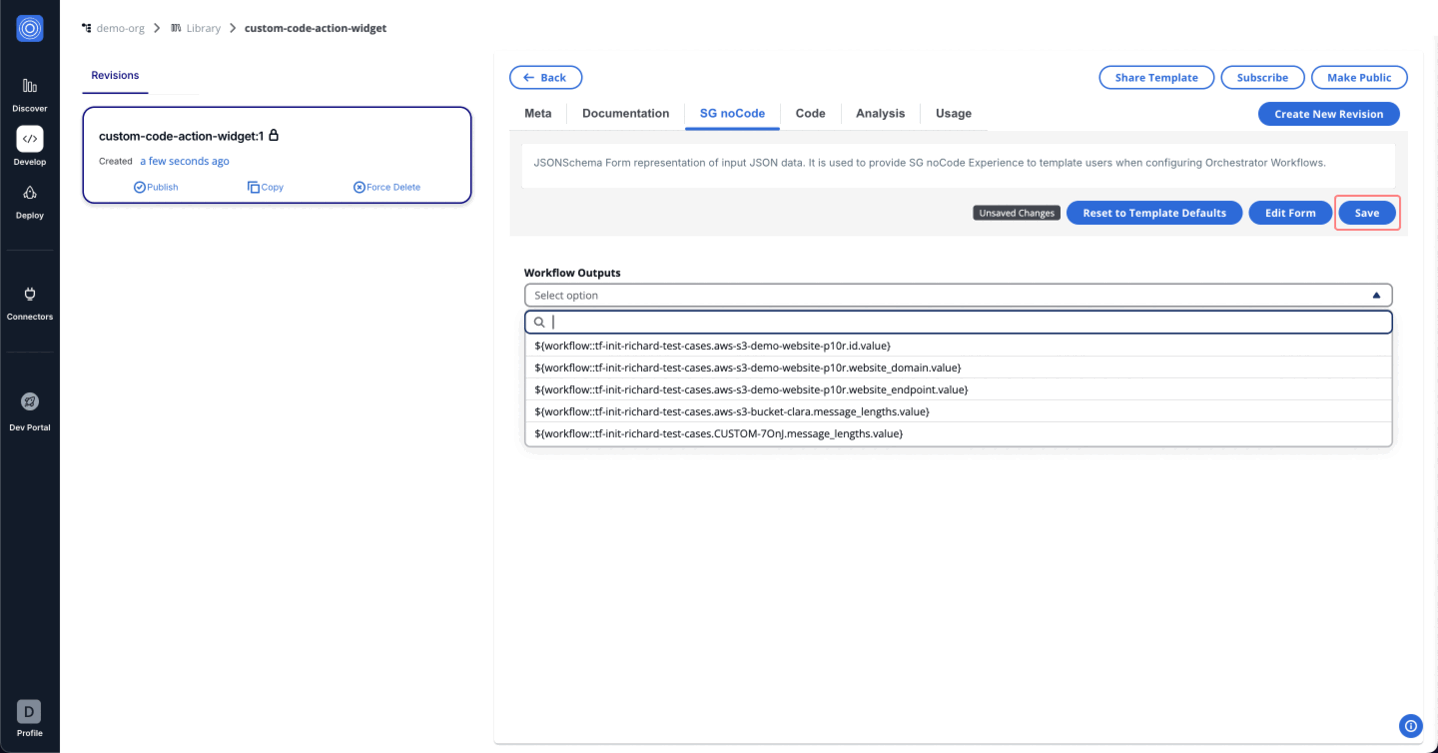
Users provide custom JavaScript code in the apiSchema.handler configuration. This code is executed directly in the frontend (in the user's browser) to process data and dynamically update the jsonSchema and uiSchema of the form.
Accessible Variables in JS Code
sg_context:viewContext: Contains contextual keys likeorg,wfgrp,stack,wf.token: User's authentication token for making secure API calls.user: Provides user details, such as email and role.triggerInfo: Contains information about the trigger of code execution, including:- triggerType: Specifies the type of trigger that initiated the code execution, such as "onSelection" or "onLoadItems".
- valueSelected: Present only when "triggerType" is "onSelection", representing the value selected by the user during execution.
- Form GUI
- Form JSON Schema
- UI Schema
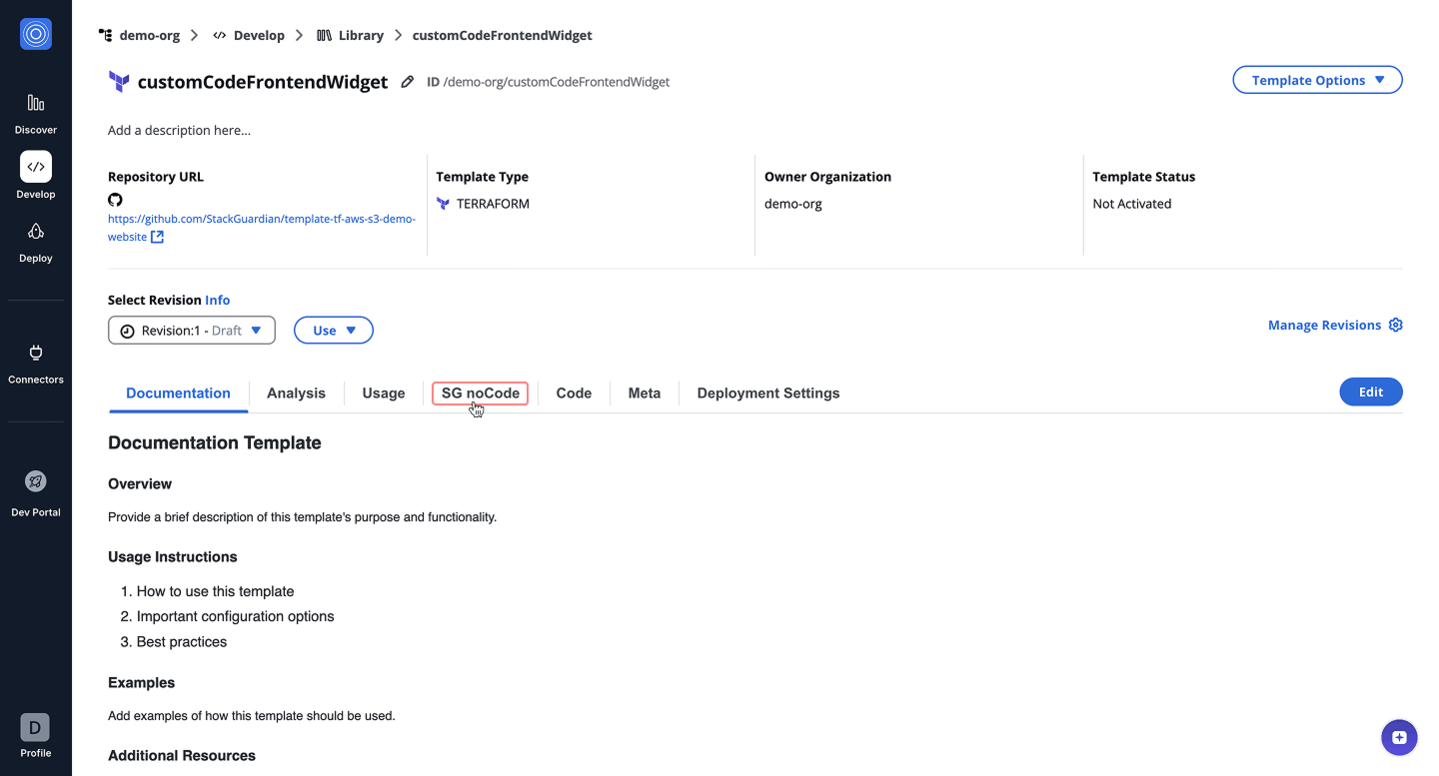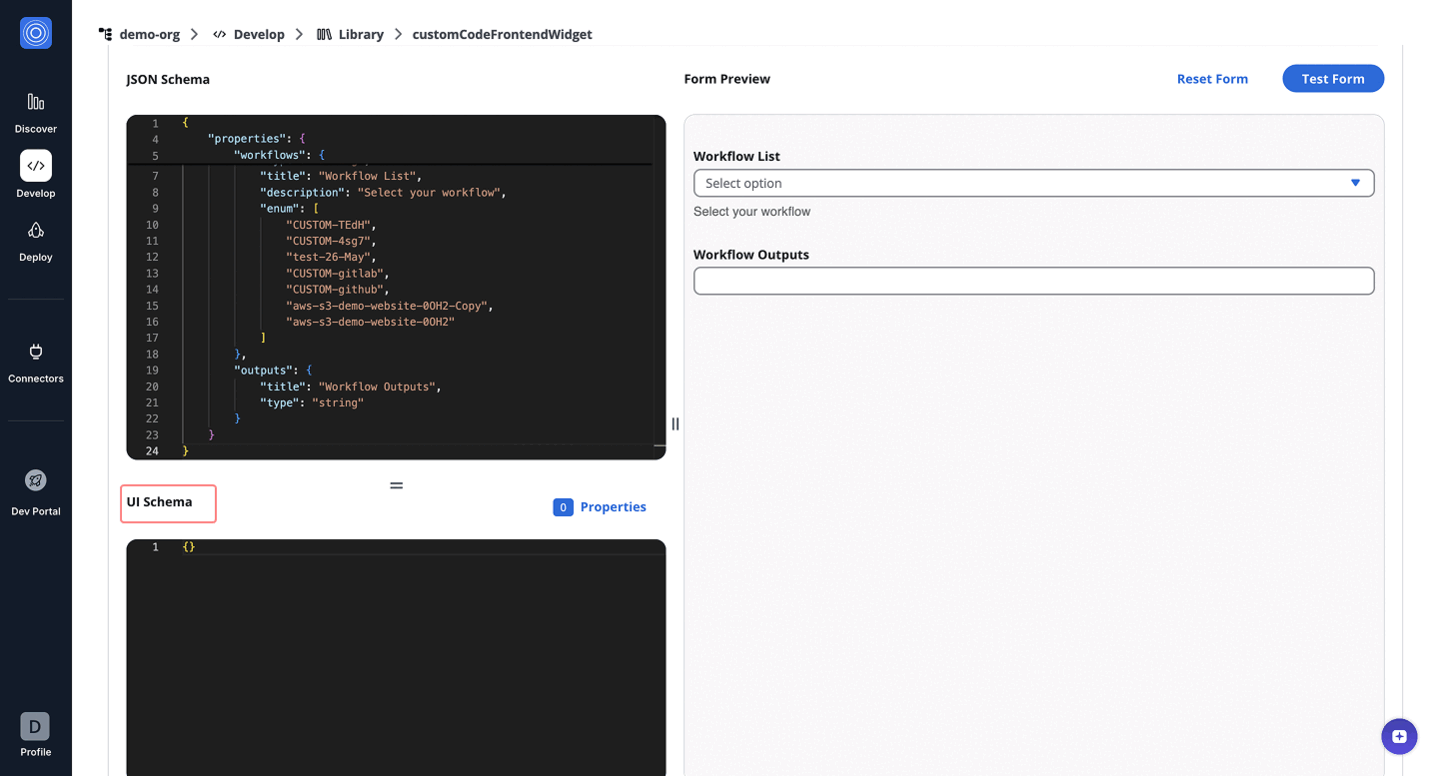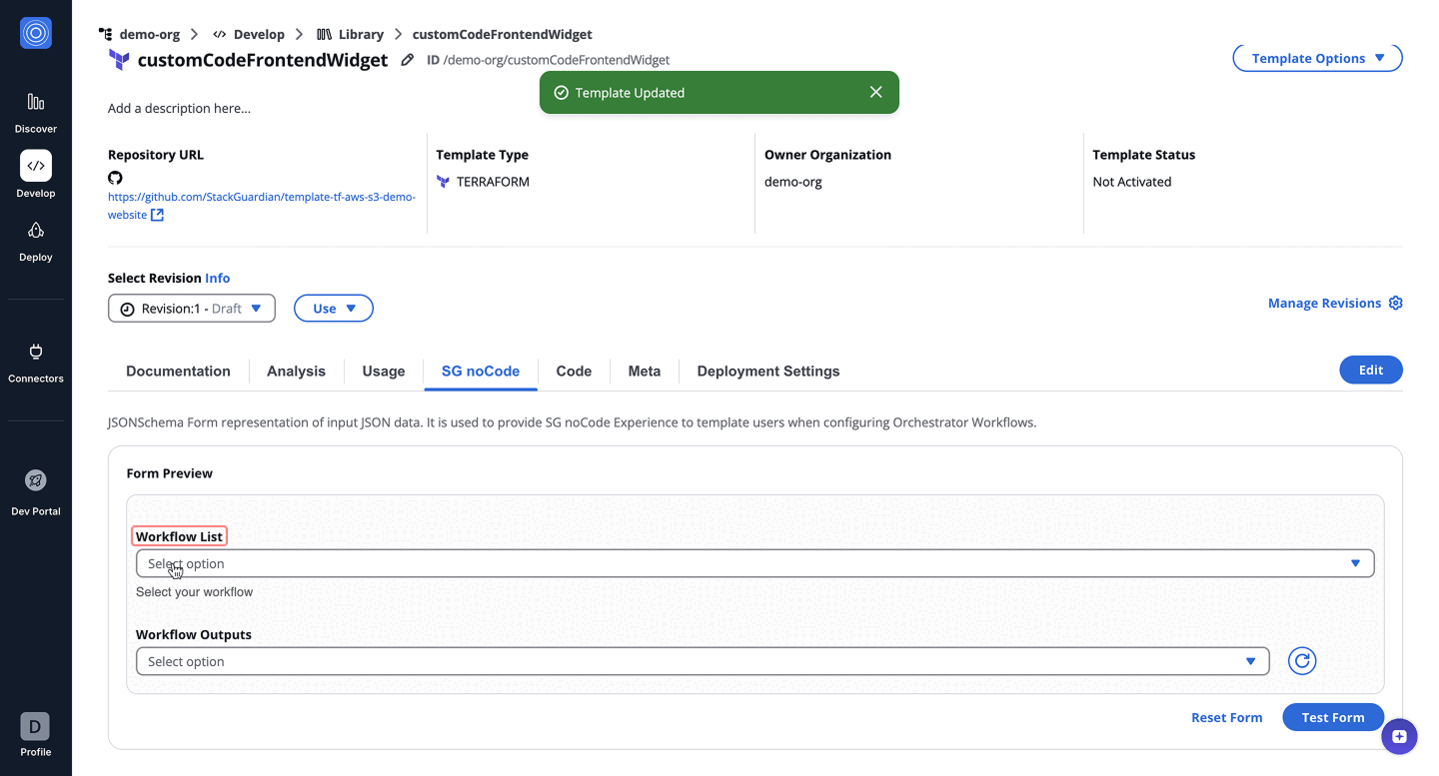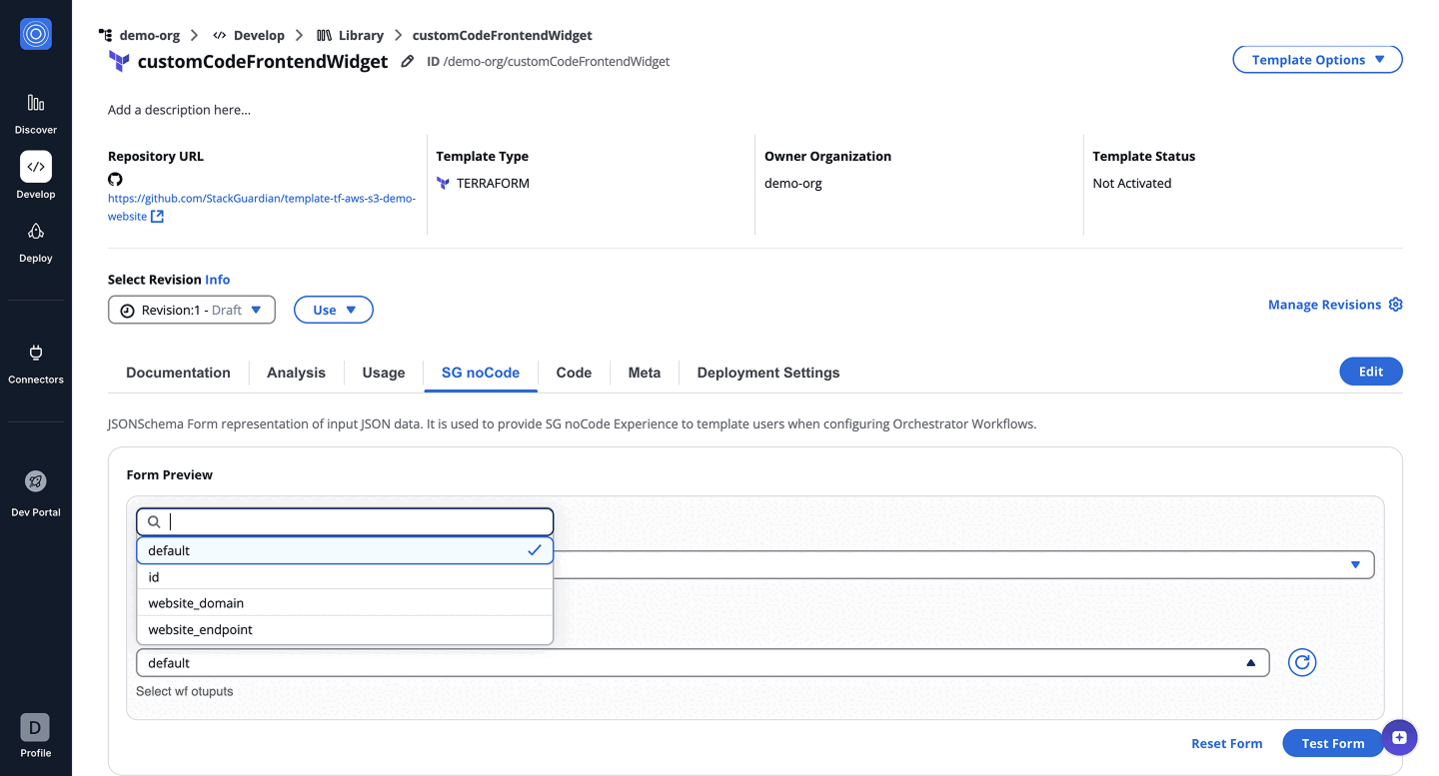
{
"$schema": "http://json-schema.org/schema#",
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"workflows": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Workflow List",
"description": "Select your workflow",
"enum": [
"CUSTOM-TEdH",
"CUSTOM-4sg7",
"test-26-May",
"CUSTOM-gitlab",
"CUSTOM-github",
"aws-s3-demo-website-0OH2-Copy",
"aws-s3-demo-website-0OH2"
]
},
"outputs": {
"title": "Workflow Outputs",
"type": "string"
}
}
}
{
"workflows": {
"ui:widget": "select"
},
"outputs": {
"ui:widget": "CustomCodeFrontendWidget",
"apiSchema": {
"triggerType": [
"onLoadItems"
],
"handler": "// Base API URL\nconst baseUrl = \"https://testapi.qa.stackguardian.io\";\n\n// Extract org and wfgrp from sg_context\nlet orgName = sg_context?.viewContext?.org || 'demo-org';\nlet wfGrpName = sg_context?.viewContext?.wfgrp || 'demo-wf-group-1';\n\n// Extract token from sg_context\nlet token = sg_context?.token;\n\nlet outputs_ = [{value:\"default\"}];\n\nconst outputsUrl = `${baseUrl}/api/v1/orgs/${orgName}/wfgrps/${wfGrpName}/wfs/${sg_context.formData.workflows}/outputs/`;\n\nconst outputsResponse = await fetch(outputsUrl, {\n headers: {\n Authorization: token\n }\n });\n\nconst outputsData = await outputsResponse.json();\nconst url = outputsData?.data?.outputs_signed_url || \"\";\n\nlet res;\nif(url){\n try{\n const res_ = await fetch(url);\n const outputsData = await res_.json();\n res = outputsData;\n }\n catch(err){\n res_={}\n }\n \n}\n\nconst keys = Object.keys(res||{});\nkeys?.forEach((op) => {\n outputs_.push({value : op})\n})\n\n// Define the modified JSON Schema\nlet modifiedJsonSchema = {\n ...sg_context.jsonSchema,\n properties: {\n ...sg_context.jsonSchema?.properties,\n outputs: {\n type: 'string',\n title: 'Choose Wf Outputs',\n description: 'Select wf otuputs',\n \"default\": sg_context.formData?.workflows,\n enum: outputs_?.length > 0 ? outputs_.map(item => item.value) : [] // Unique enum values\n }\n }\n};\n\n// Create UI Schema\nconst modifiedUISchema = {\n ...sg_context.uiSchema\n};\n\n\n\n// Return the schemas\nreturn {\n jsonSchema: modifiedJsonSchema,\n uiSchema: modifiedUISchema\n};"
}
}
}
The code dynamically fetches workflow outputs based on the context (org, workflow group, and stack) and populates a dropdown field in the form with those outputs. [ Update this as per above code logic and code below]
// Base API URL
const baseUrl = 'https://testapi.qa.stackguardian.io';
// Extract params from sg_context
let orgName = sg_context?.viewContext?.org || 'demo-org';
let wfGrpName = sg_context?.viewContext?.wfgrp || 'tf-init-richard-test-cases';
let stackName = sg_context?.viewContext?.stack || '';
let stackId = stackName ? `/stacks/${stackName}` : '';
let token = sg_context?.token;
let finalOptions = [];
// API URL to fetch workflows
let apiUrl = `${baseUrl}/api/v1/orgs/${orgName}/wfgrps/${wfGrpName}${stackId}/wfs/listall/`;
const api_response = await fetch(apiUrl, {
headers: {
Authorization: `${token}`,
},
});
// Parse JSON response
let listallWfs = await api_response.json();
// Iterate over workflows to fetch outputs
for (let i = 0; i < listallWfs.msg.length; i++) {
try {
let item = listallWfs.msg[i];
let wfName = item.ResourceName;
let wfOutputUrl = `${baseUrl}/api/v1/orgs/${orgName}/wfgrps/${wfGrpName}${stackId}/wfs/${wfName}/outputs/`;
// Fetch output
let outputResponse = await fetch(wfOutputUrl, {
headers: {
Authorization: `${token}`,
},
});
let wfData = await outputResponse.json();
let wfOutputs = wfData?.data?.outputs || {};
// Populate dropdown options
Object.keys(wfOutputs).forEach((key) => {
finalOptions.push({
label: `${wfGrpName}.${stackName}.${wfName}.${key}.value`,
value: `${wfGrpName}.${stackName}.${wfName}.${key}.value`,
});
});
} catch (e) {
console.error(e);
}
}
// Update jsonSchema and uiSchema
let modifiedUISchema = { workflow_output: { 'ui:widget': 'select' } };
let modifiedJsonSchema = { type: 'object', properties: {} };
modifiedJsonSchema.properties['workflow_output'] = {
type: 'string',
title: 'Workflow Outputs',
enum: finalOptions.map((item) => item.value),
};
return { jsonSchema: modifiedJsonSchema, uiSchema: modifiedUISchema };
8. CustomCodeWidget
The CustomCodeWidget enables dynamic and context-aware customization of form fields in real-time. By executing custom JavaScript (JS) code in a Node.js v20 runtime environment, it allows users to fetch, process, and populate form data dynamically.
Key Features
- Dynamic Data Fetching: Fetch data from APIs or other sources in real-time.
- Custom JavaScript Support: Users can write custom JS code to handle data processing and form updates.
- Runtime Environment: Executes in a Node.js v20 environment with pre-configured capabilities.
- Contextual Awareness: Leverages variables like
sg_contextfor details such asorg,wfgrp,stack, andwf.
How It Works
Users provide custom JavaScript code in the apiSchema.handler configuration. This code is executed to process data and dynamically update the jsonSchema and uiSchema of the form.
Accessible Variables in JS Code
sg_context:viewContext: Contains contextual keys likeorg,wfgrp,stack,wf.token: User's authentication token for making secure API calls.user: Provides user details, such as email and role.triggerInfo: Contains information about the trigger of code execution, including:- triggerType: Specifies the type of trigger that initiated the code execution, such as "onSelection" or "onLoadItems".
- valueSelected: Present only when "triggerType" is "onSelection", representing the value selected by the user during execution.
deploymentPlatformConfig: Contains configurations for the selected connector, if applicable.
- Form GUI
- Form JSON Schema
- UI Schema
{
"$schema": "http://json-schema.org/schema#",
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"workflow_output": {
"title": "Workflow Outputs",
"type": "string"
}
}
}
{
"workflow_output": {
"ui:widget": "CustomCodeWidget",
"ui:title": "Workflow Outputs",
"apiSchema": {
"triggerType": ["onLoadItems"],
"handler": "// Base API URL\n" +
"const baseUrl = 'https://testapi.qa.stackguardian.io';\n" +
"\n" +
"// Extract params from sg_context\n" +
"let orgName = sg_context?.viewContext?.org || 'demo-org';\n" +
"let wfGrpName = sg_context?.viewContext?.wfgrp || 'tf-init-richard-test-cases';\n" +
"let stackName = sg_context?.viewContext?.stack || '';\n" +
"let stackId = stackName ? `/stacks/${stackName}` : '';\n" +
"let token = sg_context?.token;\n" +
"\n" +
"let finalOptions = [];\n" +
"\n" +
"// API URL to fetch workflows\n" +
"let apiUrl = `${baseUrl}/api/v1/orgs/${orgName}/wfgrps/${wfGrpName}${stackId}/wfs/listall/`;\n" +
"const api_response = await fetch(apiUrl, {\n" +
" headers: {\n" +
" Authorization: `${token}`\n" +
" }\n" +
"});\n" +
"\n" +
"// Parse JSON response\n" +
"let listallWfs = await api_response.json();\n" +
"\n" +
"// Iterate over workflows to fetch outputs\n" +
"for (let i = 0; i < listallWfs.msg.length; i++) {\n" +
" try {\n" +
" let item = listallWfs.msg[i];\n" +
" let wfName = item.ResourceName;\n" +
" let wfOutputUrl = `${baseUrl}/api/v1/orgs/${orgName}/wfgrps/${wfGrpName}${stackId}/wfs/${wfName}/outputs/`;\n" +
" let outputResponse = await fetch(wfOutputUrl, {\n" +
" headers: {\n" +
" Authorization: `${token}`\n" +
" }\n" +
" });\n" +
" let wfData = await outputResponse.json();\n" +
" let wfOutputs = wfData?.data?.outputs || {};\n" +
"\n" +
" Object.keys(wfOutputs).forEach(key => {\n" +
" finalOptions.push({\n" +
" label: `${wfGrpName}.${stackName}.${wfName}.${key}.value`,\n" +
" value: `${wfGrpName}.${stackName}.${wfName}.${key}.value`\n" +
" });\n" +
" });\n" +
" } catch (e) {\n" +
" console.log(e);\n" +
" }\n" +
"}\n" +
"\n" +
"// Update jsonSchema and uiSchema\n" +
"let modifiedUISchema = { workflow_output: { 'ui:widget': 'select' } };\n" +
"let modifiedJsonSchema = { type: 'object', properties: {} };\n" +
"modifiedJsonSchema.properties['workflow_output'] = {\n" +
" type: 'string',\n" +
" title: 'Workflow Outputs',\n" +
" enum: finalOptions.map(item => item.value)\n" +
"};\n" +
"return { jsonSchema: modifiedJsonSchema, uiSchema: modifiedUISchema };"
}
}
}
The code dynamically fetches workflow outputs based on the context (org, workflow group, and stack) and populates a dropdown field in the form with those outputs.
// Base API URL
const baseUrl = 'https://testapi.qa.stackguardian.io';
// Extract params from sg_context
let orgName = sg_context?.viewContext?.org || 'demo-org';
let wfGrpName = sg_context?.viewContext?.wfgrp || 'tf-init-richard-test-cases';
let stackName = sg_context?.viewContext?.stack || '';
let stackId = stackName ? `/stacks/${stackName}` : '';
let token = sg_context?.token;
let finalOptions = [];
// API URL to fetch workflows
let apiUrl = `${baseUrl}/api/v1/orgs/${orgName}/wfgrps/${wfGrpName}${stackId}/wfs/listall/`;
const api_response = await fetch(apiUrl, {
headers: {
Authorization: `${token}`,
},
});
// Parse JSON response
let listallWfs = await api_response.json();
// Iterate over workflows to fetch outputs
for (let i = 0; i < listallWfs.msg.length; i++) {
try {
let item = listallWfs.msg[i];
let wfName = item.ResourceName;
let wfOutputUrl = `${baseUrl}/api/v1/orgs/${orgName}/wfgrps/${wfGrpName}${stackId}/wfs/${wfName}/outputs/`;
// Fetch output
let outputResponse = await fetch(wfOutputUrl, {
headers: {
Authorization: `${token}`,
},
});
let wfData = await outputResponse.json();
let wfOutputs = wfData?.data?.outputs || {};
// Populate dropdown options
Object.keys(wfOutputs).forEach((key) => {
finalOptions.push({
label: `${wfGrpName}.${stackName}.${wfName}.${key}.value`,
value: `${wfGrpName}.${stackName}.${wfName}.${key}.value`,
});
});
} catch (e) {
console.error(e);
}
}
// Update jsonSchema and uiSchema
let modifiedUISchema = { workflow_output: { 'ui:widget': 'select' } };
let modifiedJsonSchema = { type: 'object', properties: {} };
modifiedJsonSchema.properties['workflow_output'] = {
type: 'string',
title: 'Workflow Outputs',
enum: finalOptions.map((item) => item.value),
};
return { jsonSchema: modifiedJsonSchema, uiSchema: modifiedUISchema };
These custom UI widgets enhance the user experience by providing more flexibility and functionality in form creation. By leveraging these widgets, users can create more interactive and dynamic forms tailored to their specific needs.